Introduction to the Death Protection Component of Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers both death protection and a cash value component. The death protection component provides a lump sum payment to your beneficiaries upon your death. The cash value component grows over time and can be used for a variety of purposes, such as retirement, education, or emergencies.
The death protection component of universal life insurance is an important part of your financial plan. It ensures that your loved ones will be financially secure in the event of your death. The death benefit can be used to pay for funeral expenses, outstanding debts, and other expenses. It can also provide your beneficiaries with a financial cushion to help them adjust to your loss.
How the Death Protection Component Works
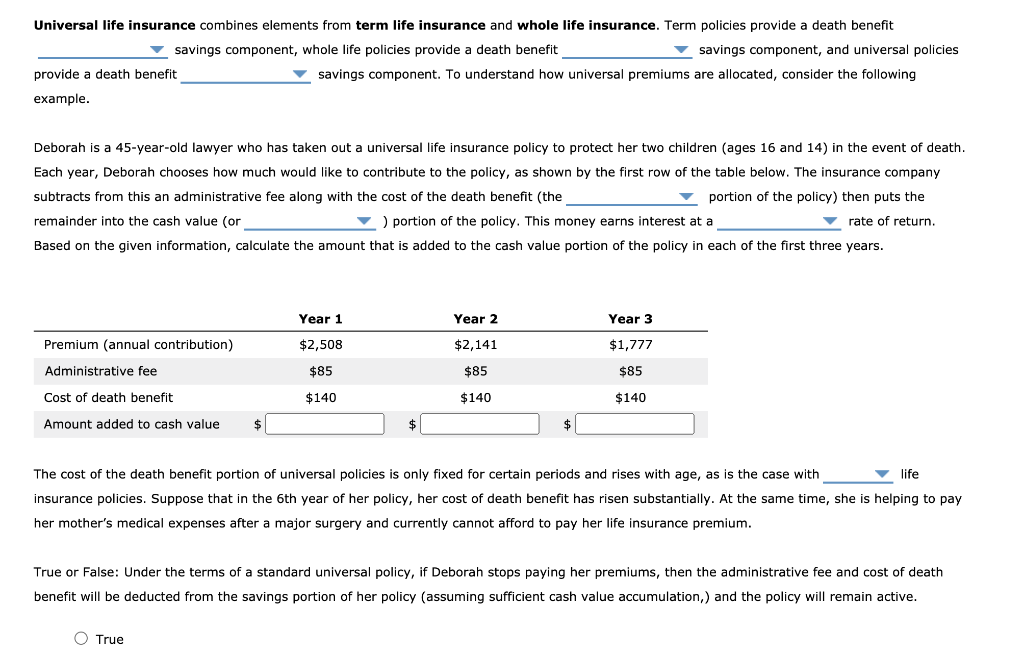
The death protection component of universal life insurance provides a financial safety net for your loved ones in the event of your untimely demise. Upon your passing, the policy will pay out a death benefit to your designated beneficiaries, ensuring their financial stability and well-being.
The death benefit is typically equal to the face amount of the policy, which is the amount of coverage you select when you purchase the policy. However, the cash value of the policy, which grows over time through interest accumulation and premium payments, can also impact the payout. If the cash value exceeds the face amount, the death benefit will be increased by the difference.
In addition to the basic death benefit, universal life insurance policies often offer additional riders or features that enhance the death protection. These may include:
- Accidental death benefit: Provides an additional payout if the insured dies due to an accident.
- Waiver of premium rider: Exempts the policyholder from paying premiums if they become disabled.
- Terminal illness rider: Allows the policyholder to access a portion of the death benefit if they are diagnosed with a terminal illness.
By understanding how the death protection component works, you can make informed decisions about the coverage you need to protect your loved ones’ financial future.
Benefits of the Death Protection Component
The death protection component of universal life insurance provides several key benefits that can help secure the financial future of your loved ones.
Financial Security for Beneficiaries
One of the primary benefits of the death protection component is the financial security it provides to your beneficiaries. In the event of your untimely death, the death benefit will be paid out to your designated beneficiaries, ensuring that they have the resources they need to maintain their financial stability. This can help cover expenses such as mortgage payments, education costs, and living expenses, providing peace of mind and reducing the financial burden on your loved ones during a difficult time.
Coverage of End-of-Life Expenses and Debts
The death protection component can also help cover end-of-life expenses and debts, such as funeral costs, medical bills, and outstanding loans. By ensuring that these expenses are taken care of, you can help prevent your family from having to deal with additional financial stress during a time of grief.
Estate Planning and Inheritance
The death protection component can play a role in estate planning and inheritance. By providing a lump sum payment to your beneficiaries, you can help ensure that your assets are distributed according to your wishes. This can be particularly beneficial if you have specific bequests or charitable donations that you want to make.
Considerations and Limitations
The cost and coverage of the death protection component of universal life insurance are influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about the coverage you need.
One key factor is your age. The younger you are, the lower your premiums will typically be. This is because younger individuals are considered lower risks for mortality. As you age, your premiums will increase to reflect the higher risk of death.
Coverage Amount
Determining the appropriate coverage amount for your death protection component is crucial. It should be sufficient to cover your final expenses, outstanding debts, and provide financial security for your loved ones. Consider the following factors when evaluating your coverage amount:
- Funeral and burial expenses
- Outstanding debts (e.g., mortgage, credit cards, loans)
- Income replacement for your family
- Educational expenses for your children
- Other financial obligations
Remember, the coverage amount should be adjusted periodically to account for inflation and changes in your financial situation.
Exclusions and Limitations
Universal life insurance death protection components typically have certain exclusions and limitations. These may include:
- Death resulting from suicide within a specific period (e.g., two years) after the policy is issued
- Death resulting from high-risk activities (e.g., skydiving, scuba diving)
- Death resulting from illegal activities
It is essential to be aware of these exclusions and limitations when selecting your coverage.
Alternatives to the Death Protection Component
While the death protection component of universal life insurance offers certain advantages, it’s essential to be aware of alternative life insurance options that provide death protection.
Two primary alternatives are term life insurance and whole life insurance. Each option has its own unique characteristics, pros, and cons.
Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. Premiums are typically lower compared to universal life insurance, making it a more affordable option in the short term.
- Pros: Lower premiums, simplicity, and no cash value accumulation.
- Cons: Coverage expires at the end of the term, and renewal premiums can be significantly higher.
Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance offers permanent coverage throughout the policyholder’s lifetime. It also accumulates a cash value that grows over time. However, premiums are typically higher than term life insurance.
- Pros: Permanent coverage, cash value accumulation, and potential for dividend payments.
- Cons: Higher premiums, slower cash value growth, and limited flexibility compared to universal life insurance.
Choosing the Best Option
The best life insurance option depends on individual needs and circumstances. Consider factors such as age, health, financial goals, and risk tolerance.
- Younger individuals with limited financial resources may prefer term life insurance for its affordability.
- Individuals seeking long-term protection and the potential for cash value growth may opt for whole life insurance.
- Those who value flexibility and customization may find universal life insurance a suitable option.
Conclusion
The death protection component of universal life insurance provides a valuable safety net for your loved ones. It ensures that your beneficiaries will receive a financial cushion in the event of your untimely demise, allowing them to cover expenses, pay off debts, and maintain their standard of living.
Remember, the death protection component is an essential part of a comprehensive financial plan. By understanding its benefits and limitations, you can make informed decisions about the coverage you need to protect your family’s financial future.
For further guidance, consider consulting with a financial professional who can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances and financial goals.