Understanding Mutual Insurance Companies
Mutual insurance companies are unique entities in the insurance industry, characterized by their distinct structure and ownership model. Unlike traditional insurance companies, mutual insurance companies are owned by their policyholders, who share in the profits and losses of the company.
Policyholders in mutual insurance companies play a vital role in the company’s operations. They have the right to vote on important decisions, such as the election of the governing body and the approval of financial statements. This participatory approach ensures that the company is run in the best interests of its policyholders.
Role of Policyholders
The role of policyholders in mutual insurance companies extends beyond their financial stake in the company. They are also actively involved in the company’s decision-making process. Policyholders have the right to:
- Attend and participate in annual meetings.
- Vote on the election of the governing body.
- Approve financial statements and make changes to the company’s bylaws.
- Submit proposals for changes to the company’s operations.
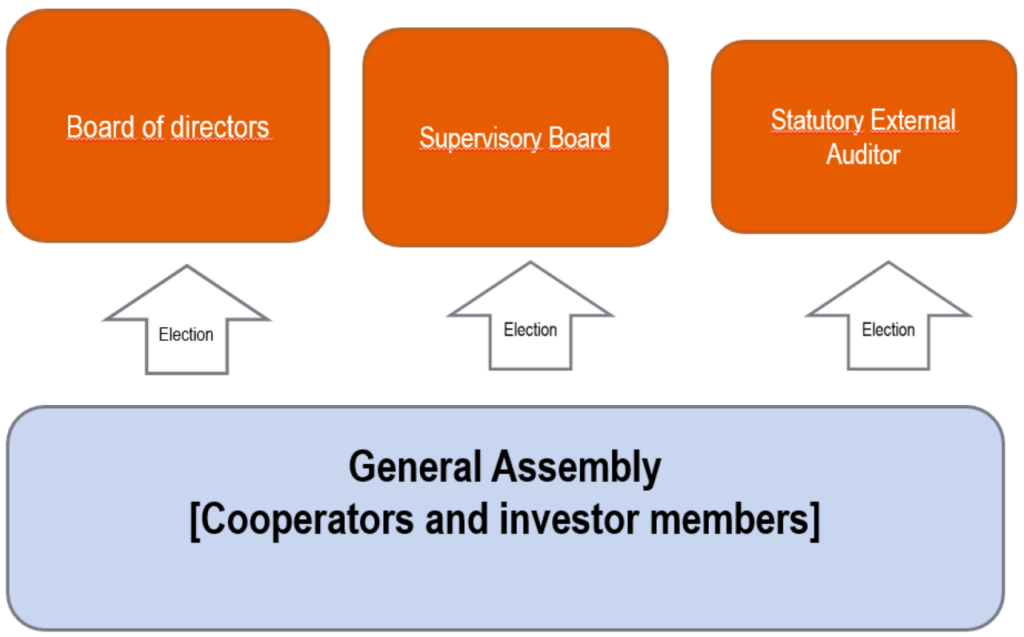
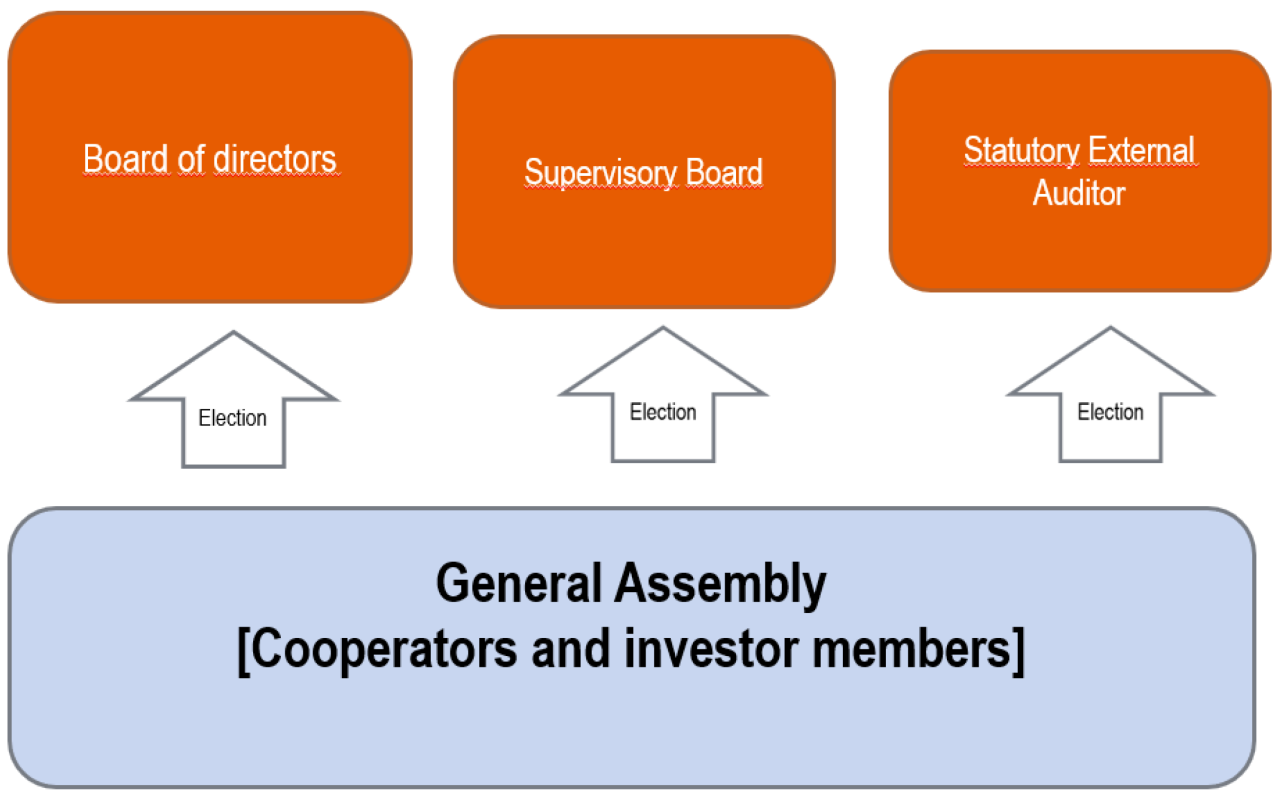
Governing Body of Mutual Insurance Companies
The governing body of a mutual insurance company is the group of individuals responsible for overseeing the company’s operations and ensuring that it is run in the best interests of its policyholders.
The governing body has a number of important functions and responsibilities, including:
- Setting the company’s overall strategic direction
- Approving the company’s budget
- Appointing and overseeing the company’s management team
- Ensuring that the company complies with all applicable laws and regulations
The composition and structure of the governing body of a mutual insurance company varies from company to company. However, most governing bodies are made up of a mix of policyholders and other stakeholders, such as employees, agents, and community leaders.
Composition of the Governing Body
The composition of the governing body of a mutual insurance company is determined by the company’s bylaws. In general, the governing body must be composed of a majority of policyholders. However, some companies also allow other stakeholders, such as employees, agents, and community leaders, to serve on the governing body.
Structure of the Governing Body
The structure of the governing body of a mutual insurance company is also determined by the company’s bylaws. In general, the governing body is headed by a chairman or president. The governing body may also have a number of committees, such as an executive committee, a finance committee, and an audit committee.
Election Process for the Governing Body
The election process for the governing body of a mutual insurance company ensures that the individuals representing the interests of the policyholders are chosen in a fair and transparent manner.
To be eligible for election to the governing body, candidates typically must meet specific criteria, such as being a policyholder in good standing, having a certain level of experience in the insurance industry, and possessing strong leadership and decision-making skills.
Voting Procedures and Role of Policyholders
The voting process for electing the governing body varies depending on the company’s bylaws and applicable regulations. Typically, each policyholder is entitled to one vote, regardless of the number of policies they hold. Voting can be conducted in person at annual meetings, by mail, or electronically.
Policyholders play a crucial role in the election process by exercising their voting rights and ensuring that the governing body represents their interests and values. Active participation in the election process helps strengthen the mutual insurance model and promotes accountability and transparency.
Types of Governing Body Structures
The governing body of a mutual insurance company can take various forms, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The choice of structure depends on factors such as the size of the company, the complexity of its operations, and the preferences of its members.
The most common types of governing body structures are:
Board of Directors
- A board of directors is a group of individuals elected by the members of the mutual insurance company to oversee its operations. The board is responsible for setting the company’s strategic direction, approving its financial plans, and ensuring that it is operating in accordance with its bylaws.
- Advantages of a board of directors include the ability to bring together a diverse group of perspectives and expertise, the ability to make decisions quickly and efficiently, and the ability to provide oversight of the company’s operations.
- Disadvantages of a board of directors include the potential for conflicts of interest, the potential for the board to become too powerful, and the potential for the board to be out of touch with the needs of the members.
Representative Assembly
- A representative assembly is a group of individuals elected by the members of the mutual insurance company to represent their interests. The assembly is responsible for setting the company’s strategic direction, approving its financial plans, and ensuring that it is operating in accordance with its bylaws.
- Advantages of a representative assembly include the ability to ensure that the members have a voice in the governance of the company, the ability to make decisions that are responsive to the needs of the members, and the ability to provide oversight of the company’s operations.
- Disadvantages of a representative assembly include the potential for the assembly to become too large and unwieldy, the potential for the assembly to be dominated by a small group of members, and the potential for the assembly to be unable to make decisions quickly and efficiently.
Combination Structure
- A combination structure is a hybrid of the board of directors and representative assembly models. In a combination structure, a board of directors is elected by the members of the mutual insurance company to oversee its operations. The board is then responsible for appointing a representative assembly to represent the interests of the members.
- Advantages of a combination structure include the ability to combine the advantages of both the board of directors and representative assembly models. This structure can provide a balance of power between the board and the members, and it can ensure that the members have a voice in the governance of the company.
- Disadvantages of a combination structure include the potential for the board to become too powerful, the potential for the assembly to become too large and unwieldy, and the potential for the two bodies to be unable to work together effectively.
Best Practices for Governing Body Elections
Ensuring fair and transparent elections for the governing body of a mutual insurance company is crucial for maintaining the integrity and accountability of the organization. Here are some best practices to consider:
Transparency and Disclosure: Provide clear and accessible information about the election process, including the eligibility criteria, nomination procedures, and voting rules. Make all relevant documents available to members.
Independent Oversight
Establish an independent oversight body, such as an election committee or third-party auditor, to ensure the impartiality and integrity of the election process. This body should have the authority to review nominations, verify votes, and address any disputes.
Accountability Measures
Implement accountability measures to hold elected officials responsible for their actions. This may include regular reporting requirements, performance evaluations, and the ability for members to recall board members if necessary.
Effective Election Processes
Examples of effective election processes include:
- Electronic Voting: Allows for secure and convenient voting from anywhere.
- Proxy Voting: Enables members to appoint a trusted representative to vote on their behalf.
- Weighted Voting: Gives members with higher insurance premiums or policyholder status more voting power.