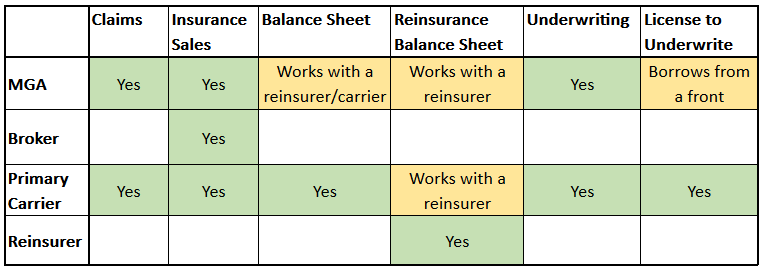
Definition of MGA in Insurance
A Managing General Agent (MGA) is an intermediary in the insurance industry that acts as a bridge between insurance companies and insurance brokers or agents.
MGAs typically specialize in a particular type of insurance, such as commercial property, casualty, or professional liability. They have the authority to underwrite and issue policies on behalf of the insurance company they represent.
Role and Responsibilities of an MGA
- Underwriting and issuing policies
- Pricing and marketing insurance products
- Managing claims
- Representing the insurance company to brokers and agents
li>Providing customer service
Types of MGA in Insurance
MGAs specialize in various insurance segments, each with unique expertise and target markets. Understanding these specializations helps insurers identify the most suitable MGA for their specific needs.
Based on their focus areas, MGAs can be categorized into different types:
Property MGAs
Property MGAs specialize in underwriting and managing property insurance policies, including homeowners’, commercial property, and renters’ insurance. They have expertise in assessing property risks, developing tailored coverage plans, and handling claims related to property damage or loss.
Casualty MGAs
Casualty MGAs focus on underwriting and managing liability insurance policies, such as general liability, professional liability, and errors and omissions insurance. They specialize in assessing liability risks, designing appropriate coverage solutions, and handling claims related to third-party injuries or damages.
Health MGAs
Health MGAs specialize in underwriting and managing health insurance policies, including individual and group health plans, dental insurance, and vision insurance. They have expertise in evaluating health risks, developing comprehensive coverage options, and handling claims related to medical expenses and healthcare services.
Specialty MGAs
Specialty MGAs underwrite and manage insurance policies for niche or specialized markets, such as aviation insurance, marine insurance, or cyber insurance. They possess in-depth knowledge of these specialized areas and cater to the unique insurance needs of specific industries or businesses.
Functions of an MGA
MGAs play a crucial role in the insurance distribution system, providing a range of functions that enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Core functions performed by MGAs include:
Underwriting
- Assess and evaluate risks to determine insurability and appropriate premium rates.
- Develop underwriting guidelines and criteria to ensure consistent and objective decision-making.
- Negotiate and bind coverage with policyholders.
Policy Issuance
- Issue policies and endorsements to policyholders.
- Ensure that policies are compliant with regulatory requirements and meet the needs of policyholders.
- Maintain accurate records of all policies issued.
Claims Handling
- Receive, investigate, and adjust claims.
- Negotiate and settle claims with policyholders and third parties.
- Manage claims reserves and ensure timely payment of claims.
Customer Service
- Provide ongoing support and assistance to policyholders.
- Respond to inquiries, resolve complaints, and maintain positive customer relationships.
- Gather feedback from policyholders to improve products and services.
Benefits of Using an MGA
Partnering with an MGA offers numerous advantages for both insurance companies and policyholders. MGAs provide a range of value-added services and expertise that can enhance insurance operations and improve outcomes.
For insurance companies, MGAs offer access to niche markets and specialized underwriting expertise. They can help insurers expand their product offerings, reach new customer segments, and optimize risk management strategies.
Benefits for Insurance Companies
- Market Access: MGAs have established relationships with brokers and distribution channels, providing insurers with access to niche markets and specialized customer segments.
- Underwriting Expertise: MGAs possess in-depth knowledge and experience in specific industry sectors or risk profiles, enabling insurers to refine their underwriting processes and improve risk selection.
- Risk Management: MGAs provide risk management services, such as claims handling, loss control, and risk assessment, helping insurers mitigate risks and enhance their overall risk management strategies.
- Operational Efficiency: MGAs can handle administrative tasks and provide operational support, allowing insurers to focus on core business activities and improve operational efficiency.
- Cost Savings: By outsourcing specific functions to MGAs, insurers can reduce overhead costs and improve their overall profitability.
Benefits for Policyholders
- Tailored Coverage: MGAs specialize in niche markets, offering customized insurance products that meet the specific needs of policyholders.
- Competitive Pricing: MGAs have access to multiple insurance carriers and can negotiate competitive rates for policyholders.
- Personalized Service: MGAs provide personalized service and support, ensuring that policyholders receive the attention and guidance they need.
- Claims Support: MGAs assist policyholders with claims handling, ensuring a smooth and efficient claims process.
- Risk Management Advice: MGAs provide risk management advice and support, helping policyholders identify and mitigate risks, reducing the likelihood and severity of losses.
Challenges Faced by MGAs
Managing General Agents (MGAs) in the insurance industry face various challenges that impact their operations and growth. These challenges include regulatory compliance, market competition, and technological advancements.
To adapt to these challenges, MGAs are innovating and exploring new strategies. They are investing in technology, forming partnerships, and expanding their product offerings to stay competitive and meet the evolving needs of the insurance market.
Regulatory Compliance
MGAs must comply with a complex and evolving regulatory landscape. They are subject to regulations from insurance regulators, such as the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), as well as state insurance departments. These regulations cover various aspects of MGA operations, including licensing, financial reporting, and risk management.
MGAs must invest significant resources to ensure compliance with these regulations. They must have robust compliance programs in place to monitor and manage their operations. Failure to comply with regulations can lead to fines, penalties, and reputational damage.
Market Competition
MGAs operate in a highly competitive market. They compete with other MGAs, as well as with insurance carriers, for business. To differentiate themselves, MGAs must offer unique and innovative products and services.
MGAs are also facing competition from InsurTech companies. These companies are using technology to disrupt the insurance industry and offer new products and services that are more convenient and affordable for consumers.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are rapidly changing the insurance industry. MGAs must invest in technology to stay competitive. They must use technology to improve their operations, automate processes, and provide better service to their customers.
MGAs are using technology to develop new products and services, such as telematics-based insurance products. They are also using technology to improve their underwriting and claims processes.
Future of MGA in Insurance
The MGA market is poised for continued growth and evolution in the coming years. Several key trends are shaping the future of MGAs in the insurance distribution ecosystem:
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in the insurance industry, and MGAs are no exception. MGAs are using technology to streamline their operations, improve their underwriting capabilities, and better serve their customers. For example, MGAs are using data analytics to identify new underwriting opportunities and to develop more targeted marketing campaigns. They are also using technology to improve their customer service, such as by providing online portals and mobile apps.
Data analytics is another important trend that is shaping the future of MGAs. MGAs are using data analytics to better understand their customers and to develop more tailored products and services. For example, MGAs are using data analytics to identify customers who are at risk of lapsing their policies. They can then target these customers with special offers or discounts to encourage them to stay with the insurer.
The regulatory landscape is also evolving, which is having an impact on the MGA market. In recent years, there has been a trend towards increased regulation of the insurance industry. This has led to increased compliance costs for MGAs, and it has also made it more difficult for MGAs to enter the market. However, MGAs that are able to adapt to the changing regulatory landscape will be well-positioned to succeed in the future.
Impact of Technology
Technology is having a major impact on the MGA market. MGAs are using technology to streamline their operations, improve their underwriting capabilities, and better serve their customers. For example, MGAs are using data analytics to identify new underwriting opportunities and to develop more targeted marketing campaigns. They are also using technology to improve their customer service, such as by providing online portals and mobile apps.
Impact of Data Analytics
Data analytics is another important trend that is shaping the future of MGAs. MGAs are using data analytics to better understand their customers and to develop more tailored products and services. For example, MGAs are using data analytics to identify customers who are at risk of lapsing their policies. They can then target these customers with special offers or discounts to encourage them to stay with the insurer.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
The regulatory landscape is also evolving, which is having an impact on the MGA market. In recent years, there has been a trend towards increased regulation of the insurance industry. This has led to increased compliance costs for MGAs, and it has also made it more difficult for MGAs to enter the market. However, MGAs that are able to adapt to the changing regulatory landscape will be well-positioned to succeed in the future.