Coverage Comparison
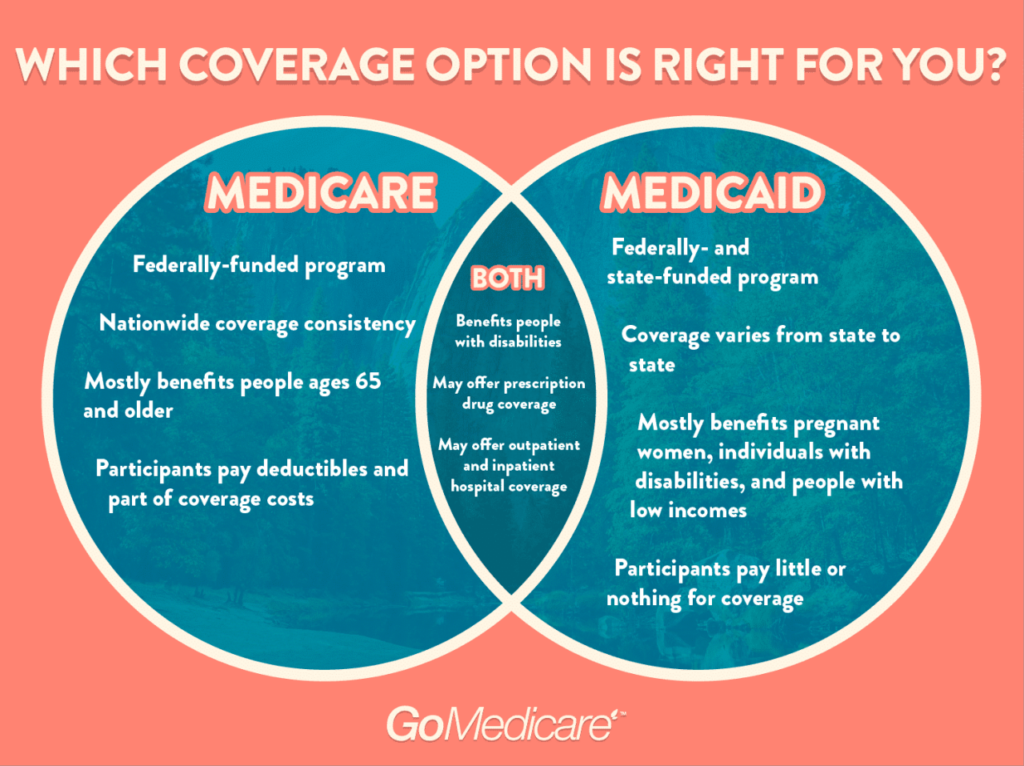
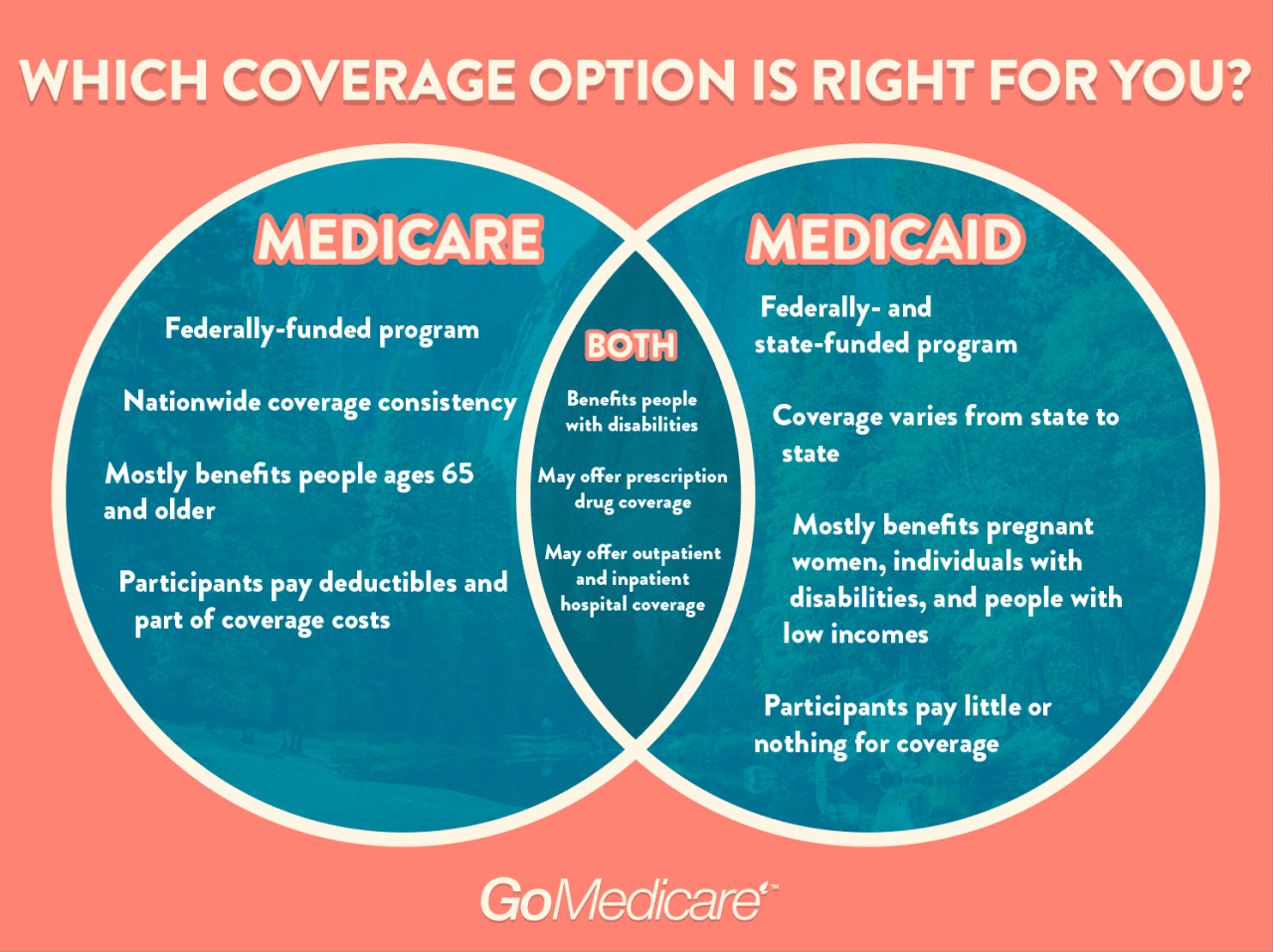
Medicaid and private insurance offer different types of coverage, affecting the range of healthcare services accessible to individuals. Medicaid, a government-funded program, primarily targets low-income individuals and families. In contrast, private insurance is obtained through employers or purchased directly from insurance companies, providing coverage to individuals and families of varying income levels.
Medicaid Coverage
Medicaid offers comprehensive coverage for essential healthcare services, including:
– Doctor visits
– Hospitalizations
– Emergency care
– Preventive care (e.g., checkups, screenings)
– Prescription drugs
– Long-term care (in some states)
Private Insurance Coverage
Private insurance plans vary in their coverage, depending on the specific policy purchased. However, most plans typically cover:
– Doctor visits
– Hospitalizations
– Emergency care
– Preventive care
– Prescription drugs
– Mental health services
– Dental and vision care (often with additional premiums)
Coverage Limitations and Exclusions
Both Medicaid and private insurance have limitations and exclusions in their coverage. Medicaid may have income and asset limits for eligibility, and coverage may vary based on the state of residence. Private insurance plans may have deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, which can impact the out-of-pocket costs for healthcare services. Additionally, both Medicaid and private insurance may have exclusions for certain services or treatments, such as cosmetic procedures or experimental treatments.
Eligibility and Enrollment
Eligibility and enrollment processes vary between Medicaid and private insurance. Understanding these differences is crucial for accessing the appropriate coverage.
Eligibility Criteria
- Medicaid: Generally available to low-income individuals, families, pregnant women, and individuals with disabilities. Eligibility requirements vary by state.
- Private Insurance: Eligibility typically based on age, employment status, and income. Coverage options may vary depending on the insurer and plan.
Enrollment Process
Enrollment processes differ between Medicaid and private insurance.
Medicaid
- Apply through state or local Medicaid agencies.
- Provide proof of identity, income, and other eligibility factors.
- Open enrollment periods vary by state.
- Special enrollment periods may be available for certain life events (e.g., pregnancy, loss of income).
Private Insurance
- Purchase coverage directly from insurance companies or through brokers.
- Provide personal and health information during application.
- Open enrollment period typically runs from November to January.
- Special enrollment periods may be available for qualifying life events (e.g., marriage, birth of a child).
Cost and Affordability
When comparing Medicaid and private insurance, it’s crucial to consider the financial implications. This includes premiums, deductibles, copayments, and potential out-of-pocket expenses.
Medicaid is generally more affordable than private insurance, as it is a government-funded program designed to provide healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. Premiums are typically low or non-existent, and deductibles and copayments are often minimal or waived.
Premiums
Medicaid premiums vary depending on the state and individual circumstances, but they are generally lower than private insurance premiums. In some cases, Medicaid may not require any premium payments at all.
Private insurance premiums, on the other hand, can vary widely depending on factors such as age, health status, and the type of coverage desired. Premiums can be hundreds or even thousands of dollars per month.
Deductibles
A deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. Medicaid deductibles are typically lower than private insurance deductibles, and they may be waived for certain services.
Private insurance deductibles can vary significantly, ranging from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. Higher deductibles typically result in lower premiums, but they also mean you will have to pay more out-of-pocket before your insurance kicks in.
Copayments
Copayments are fixed amounts you pay for certain medical services, such as doctor’s visits or prescription drugs. Medicaid copayments are typically low, and they may be waived for certain services or individuals.
Private insurance copayments can vary depending on the type of service and the insurance plan. They can range from a few dollars to hundreds of dollars per service.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses refer to the total amount you may have to pay for healthcare services, including premiums, deductibles, copayments, and any other expenses not covered by your insurance.
Medicaid typically has lower out-of-pocket expenses than private insurance, as it covers a wider range of services and has lower deductibles and copayments. However, Medicaid may have limits on certain services, and you may have to pay for some services out-of-pocket.
Private insurance out-of-pocket expenses can vary significantly depending on the type of plan and your individual healthcare needs. It’s important to carefully consider the potential out-of-pocket expenses before choosing a private insurance plan.
Financial Assistance Programs
There are several financial assistance programs available to help individuals and families with the cost of health insurance. These programs include:
- Medicaid expansion
- Premium tax credits
- Cost-sharing reductions
- Extra Help with Medicare prescription drug costs
These programs can help reduce the cost of health insurance premiums, deductibles, and copayments, making it more affordable for individuals and families to get the healthcare coverage they need.
Provider Networks
Medicaid and private insurance offer varying provider networks to their beneficiaries. Understanding the differences can help you access the healthcare services you need at the right time and cost.
Provider networks consist of healthcare providers, such as doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities, that have contracted with insurance companies or government programs to provide services to their members or beneficiaries.
In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Providers
In-network providers are healthcare providers who have agreed to provide services to members or beneficiaries of a particular insurance plan or program at negotiated rates. Using in-network providers generally results in lower out-of-pocket costs for healthcare services.
Out-of-network providers are healthcare providers who have not contracted with an insurance plan or program. Using out-of-network providers typically results in higher out-of-pocket costs, as the insurance plan may not cover the full cost of the services.
Finding In-Network Providers
To find in-network providers, you can:
- Check your insurance plan’s website or contact customer service.
- Use online provider directories or search tools provided by your insurance company.
- Ask your primary care physician or other healthcare provider for recommendations.
Benefits of Using In-Network Providers
There are several benefits to using in-network providers:
- Lower out-of-pocket costs: In-network providers have agreed to accept negotiated rates, which can result in lower out-of-pocket costs for you.
- Coverage for preventive care: In-network providers are more likely to offer preventive care services, such as screenings and checkups, at no cost to you.
- Easier access to care: In-network providers are often located closer to you and may have more convenient appointment times.
Restrictions on Access to Certain Providers or Specialists
Some insurance plans may have restrictions on access to certain providers or specialists. For example, you may need to get a referral from your primary care physician before you can see a specialist. It’s important to check with your insurance plan to understand any restrictions that may apply.
Quality of Care
When comparing Medicaid and private insurance, the quality of care provided is a crucial factor to consider. While both types of insurance aim to provide essential healthcare services, there may be variations in the quality of care received.
Factors that can affect the quality of care include:
- Provider qualifications and experience
- Patient satisfaction
- Access to specialized care
- Coordination of care
Research and data suggest that the quality of care provided by Medicaid and private insurance can vary depending on specific circumstances and geographic locations. In some cases, Medicaid patients may experience lower quality of care compared to privately insured patients due to factors such as limited access to specialists, longer wait times for appointments, and potential financial barriers to receiving certain treatments.
However, it’s important to note that the quality of care can vary significantly within both Medicaid and private insurance plans. There are many high-quality Medicaid programs that provide comprehensive healthcare services, and some private insurance plans may offer limited coverage or have restrictive provider networks.
Ultimately, the quality of care received depends on various factors, including the specific insurance plan, the healthcare providers involved, and the individual’s health needs and preferences.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Medicaid and private insurance offer different benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these differences can help individuals and families make informed decisions about their health coverage.
The following table summarizes the key advantages and disadvantages of each type of insurance:
| Factor | Medicaid | Private Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Comprehensive coverage for low-income individuals and families | Varies depending on the plan; typically more comprehensive than Medicaid |
| Cost | Low or no cost for eligible individuals | Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs |
| Provider Networks | Limited provider networks in some areas | Wider provider networks, including specialists and hospitals |
| Quality of Care | Quality of care may vary depending on provider availability | Typically higher quality of care due to access to a wider range of providers |
Medicaid may be a suitable option for individuals and families with low incomes or limited resources. Private insurance may be more appropriate for those who can afford higher premiums and deductibles and value a wider range of providers and potentially higher quality of care.