Valuation Methods
When determining the worth of an insurance book of business, multiple valuation approaches can be employed. These methods consider different aspects of the business to arrive at a fair and accurate valuation.
Income Approach
The income approach evaluates the present value of the future cash flows generated by the insurance book of business. It considers factors such as renewal premiums, commissions, and expenses to estimate the net income stream. The present value of these future cash flows is then calculated using a discount rate that reflects the risk and uncertainty associated with the business.
“The income approach focuses on the earning potential of the insurance book of business, providing insights into its profitability and sustainability.”
Factors Influencing Valuation

The valuation of an insurance book of business is influenced by a multitude of factors, including the size of the book, its loss ratio, and the quality of its underwriting.
Book Size
The size of an insurance book of business is a significant factor in its valuation. Larger books are generally more valuable than smaller books, as they represent a greater pool of potential revenue and profit. This is because larger books are more likely to be profitable due to the law of large numbers, which states that as the number of insured risks increases, the actual loss experience will approach the expected loss experience.
Loss Ratio
The loss ratio is another important factor that influences the valuation of an insurance book of business. The loss ratio is the ratio of losses incurred to premiums earned. A higher loss ratio indicates that the insurer is paying out more in claims than it is collecting in premiums, which can reduce the value of the book. Conversely, a lower loss ratio indicates that the insurer is profitable, which can increase the value of the book.
Underwriting Quality
The quality of an insurer’s underwriting is also a key factor in determining the value of its book of business. Underwriting is the process of selecting and pricing risks. Good underwriting practices can help to reduce the insurer’s loss ratio and increase its profitability. This, in turn, can increase the value of the insurer’s book of business.
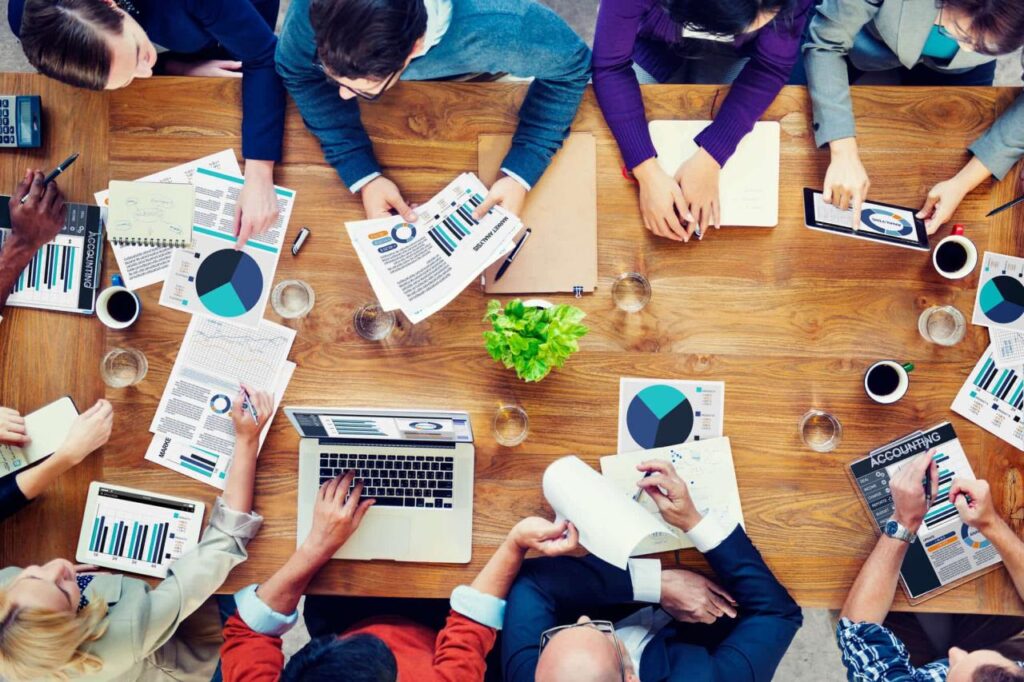
Data Collection and Analysis
The accuracy of an insurance book of business valuation hinges on the quality of data collected and analyzed. This process involves gathering relevant financial and operational information to assess the book’s value.
Data collection should be comprehensive and include historical and current data on premiums, claims, expenses, and other relevant metrics. It is essential to ensure data accuracy and consistency by using reliable sources and cross-checking information.
Data Analysis
Once data is collected, it should be analyzed to determine the book’s valuation. This involves using statistical techniques and financial models to assess the book’s profitability, growth potential, and risk profile.
Key factors to consider during data analysis include:
- Premium volume and growth trends
- Loss ratios and claims frequency
- Expense ratios and operating costs
- Underwriting profitability and risk exposure
- Market share and competitive landscape
By analyzing these factors, valuators can gain insights into the book’s historical performance and future prospects, which are crucial for determining its value.
Best Practices
To ensure the reliability and accuracy of the valuation, it is essential to follow best practices when using data:
- Use credible data sources: Rely on financial statements, actuarial reports, and other reliable sources for data.
- Verify data accuracy: Cross-check data from multiple sources and conduct reasonableness checks to ensure accuracy.
- Consider data trends: Analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns that may influence the book’s value.
- Use appropriate valuation methods: Select valuation methods that are suitable for the specific book of business and align with industry standards.
- Document the valuation process: Clearly document the data collection, analysis, and valuation methods used to support the valuation conclusion.
By adhering to these best practices, valuators can ensure that the data used to determine the value of an insurance book of business is reliable, accurate, and supports a defensible valuation conclusion.
Sensitivity Analysis and Reporting
Sensitivity analysis plays a crucial role in valuation, as it helps assess the impact of various assumptions and parameters on the final valuation outcome. By conducting sensitivity analysis, we can gain insights into how changes in key inputs affect the valuation result.
To conduct sensitivity analysis, we can use a range of techniques, including scenario analysis and Monte Carlo simulations. Scenario analysis involves evaluating different scenarios based on specific assumptions, while Monte Carlo simulations use random sampling to generate multiple valuation outcomes.
Reporting Valuation Results Effectively
Once the valuation is complete, it’s essential to report the results effectively to stakeholders. The valuation report should clearly present the assumptions, methodologies, and results in a manner that is easy to understand and interpret.
- Transparency: The report should be transparent, providing a clear explanation of the valuation process, assumptions, and limitations.
- Clarity: The results should be presented in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and summaries to enhance readability.
- Sensitivity Analysis: The report should include a sensitivity analysis section that demonstrates how changes in key assumptions impact the valuation outcome.
- Limitations and Disclaimers: The report should acknowledge any limitations or disclaimers associated with the valuation, ensuring that users understand the context and boundaries of the results.