Cost Breakdown
The cost of immunizations without insurance can vary depending on the type of vaccine, the location, and the provider. However, the following table provides a general overview of the average costs of common immunizations:
Note: These costs are subject to change and may not reflect the most up-to-date pricing. It’s always best to contact your healthcare provider or insurance company for the most accurate information.
Immunization Costs
| Vaccine | Average Cost Without Insurance |
|---|---|
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) | $150-$200 |
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (DTaP) | $100-$150 |
| Polio | $50-$100 |
| Hepatitis A | $100-$150 |
| Hepatitis B | $150-$200 |
| Human Papillomavirus (HPV) | $200-$250 |
Factors Affecting Cost
The cost of immunizations without insurance can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you plan for and manage the expenses associated with vaccinations.
The following are key factors that can influence the cost of immunizations:
Age of the Recipient
The age of the recipient can impact the cost of immunizations. Some vaccines are recommended at specific ages or during specific stages of life. For example, certain vaccines may be required for school entry or travel to certain countries. The cost of these vaccines can vary depending on the age of the recipient.
Location of the Healthcare Provider
The location of the healthcare provider can also affect the cost of immunizations. Different regions and states may have varying costs for vaccines and administration fees. Additionally, the type of healthcare facility (e.g., private clinic, community health center) can influence the cost.
Type of Vaccine Used
The type of vaccine used can significantly impact the cost of immunization. Some vaccines are more expensive to produce and administer than others. For example, live vaccines tend to be more expensive than inactivated vaccines. The specific vaccine recommended for a particular disease can also affect the cost.
Financial Assistance Options
Uninsured individuals can seek financial assistance from various programs to cover the cost of immunizations.
The following are some of the options available:
Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program
The VFC program is a federally funded program that provides free vaccines to children who are uninsured, underinsured, or Medicaid-eligible. The program covers the cost of vaccines for children from birth through age 18.
Medicaid and CHIP
Medicaid and CHIP are government health insurance programs that provide coverage for low-income individuals and families. Both programs cover the cost of immunizations.
Private Insurance Plans
Some private insurance plans cover the cost of immunizations. However, coverage may vary depending on the plan. It is important to check with your insurance provider to determine what immunizations are covered.
Importance of Immunizations
Immunizations play a crucial role in safeguarding individuals and communities from a multitude of preventable diseases. They confer numerous health benefits, ranging from personal protection to the broader impact on public health.
Vaccinations stimulate the body’s immune system to recognize and combat specific pathogens, rendering individuals less susceptible to infection. This protective shield not only shields vaccinated individuals but also helps prevent the spread of infectious diseases within communities, reducing the overall burden of illness and its associated costs.
Potential Consequences of Not Being Vaccinated
Failing to receive timely immunizations can lead to severe health consequences. Unvaccinated individuals face an increased risk of contracting preventable diseases, some of which can cause serious complications, long-term disabilities, or even death.
Measles, for instance, can result in pneumonia, encephalitis, or even death. Pertussis, commonly known as whooping cough, can lead to respiratory failure, especially in infants. Polio, once a leading cause of paralysis, can still strike unvaccinated individuals, causing permanent disability or even death.
The absence of widespread vaccination can lead to outbreaks of preventable diseases, jeopardizing the health of entire communities. This underscores the paramount importance of maintaining high immunization rates to safeguard both individuals and the public at large.
Resources for Finding Affordable Immunizations
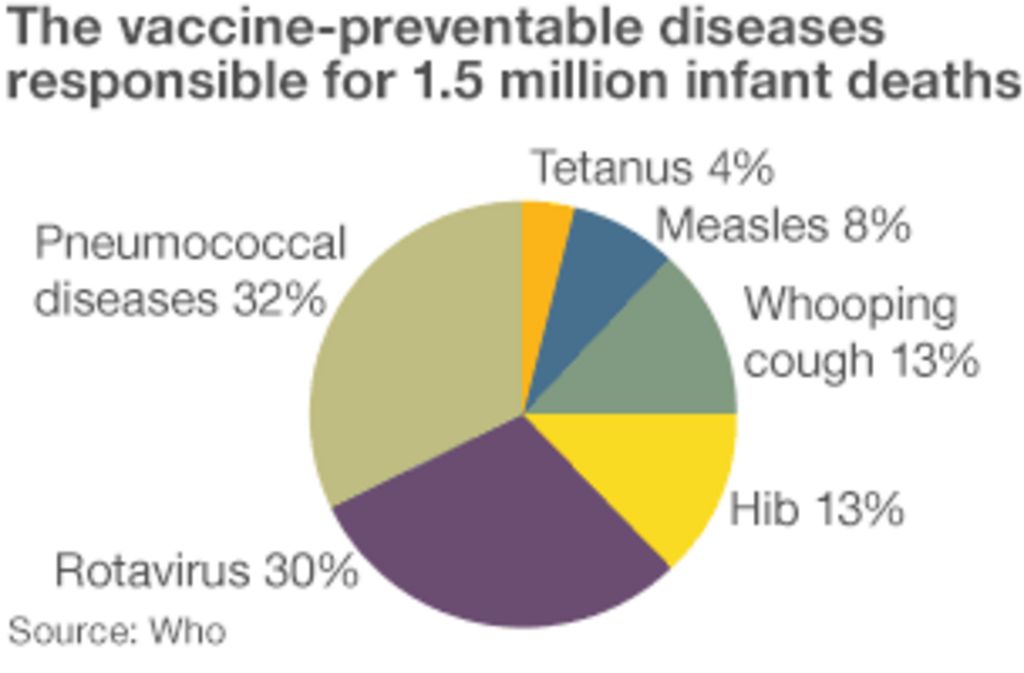
Finding affordable immunizations without insurance can be challenging, but there are resources available to help.
– Local health departments often offer immunization services at low or no cost.
– Community health centers are federally funded clinics that provide affordable healthcare, including immunizations.
– Non-profit organizations such as United Way and the American Red Cross may offer assistance with immunization costs.