Insurance Certificate Overview
A certificate of insurance is a document issued by an insurance company that verifies the existence and coverage details of an insurance policy. It serves as proof of insurance for individuals or businesses, demonstrating that they have the necessary coverage to protect themselves and others against potential risks and liabilities.
The history of certificates of insurance can be traced back to the early days of insurance, when merchants and traders needed to prove their insurability to potential partners and customers. Over time, certificates of insurance became widely used in various industries, including construction, healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
Certificates of insurance are commonly used in situations where one party requires proof of insurance from another party. For example:
– A contractor may need to provide a certificate of insurance to a property owner before starting work.
– A healthcare provider may need to provide a certificate of insurance to a patient before providing treatment.
– A driver may need to provide a certificate of insurance to a rental car company before renting a vehicle.
Template Structure and Components
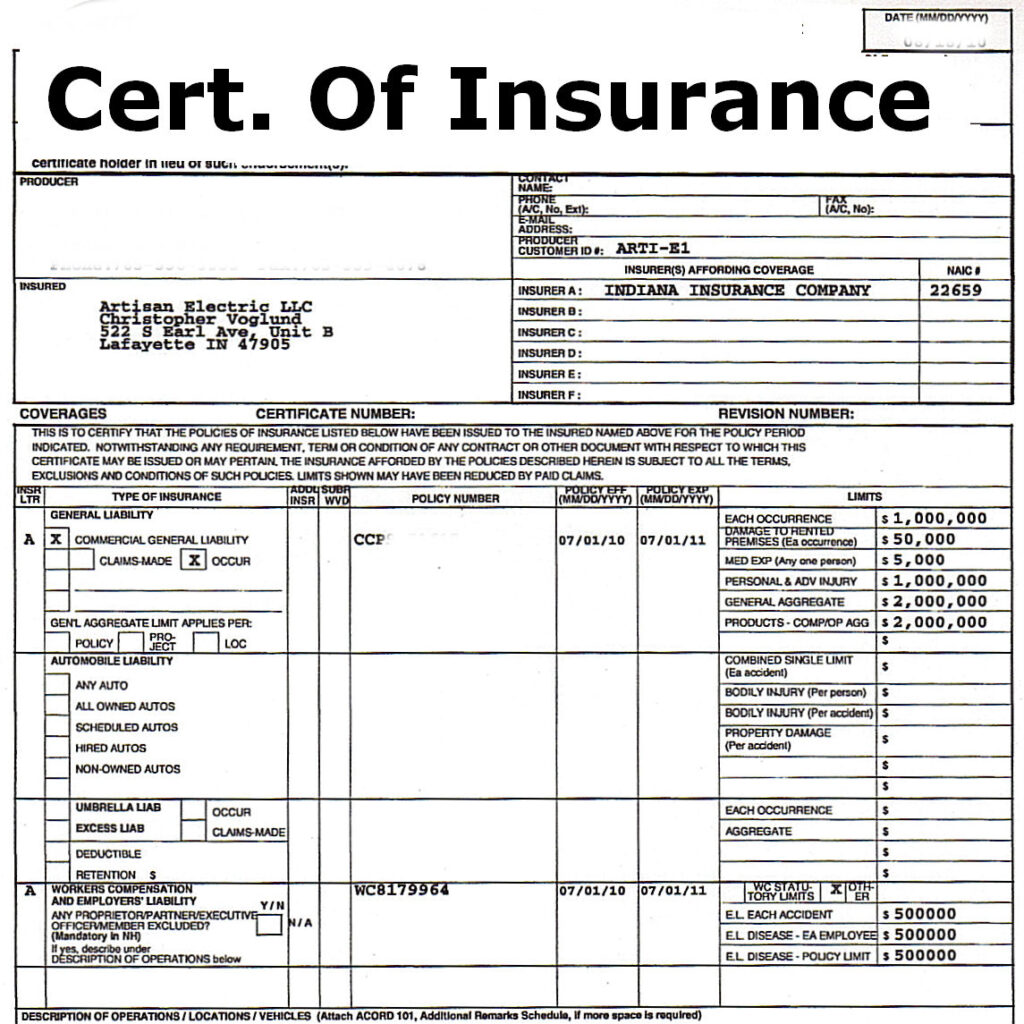
A certificate of insurance template typically follows a structured format to ensure essential information is captured and presented clearly. This structure includes several key sections, each containing specific information.
Here are the key sections of a certificate of insurance template:
Policy Information
- Policy Number: A unique identifier assigned to the insurance policy.
- Policy Period: The effective dates of the insurance coverage.
- Insurer Information: The name and contact information of the insurance company.
- Insured Information: The name and contact information of the policyholder.
- Certificate Holder: The entity requesting the certificate of insurance, often a third party.
Coverage Information
- Type of Insurance: The specific insurance coverage provided, such as general liability, professional liability, or property insurance.
- Coverage Limits: The maximum amount of coverage provided for each type of insurance.
- Deductibles: The amount that the insured is responsible for paying before the insurance coverage begins.
- Additional Insured: If applicable, the certificate may include additional parties covered under the policy.
Additional Information
- Policy Status: Whether the policy is active, canceled, or expired.
- Endorsements: Any changes or modifications to the original policy terms.
- Agent Information: The name and contact information of the insurance agent or broker who arranged the policy.
- Certificate Date: The date the certificate was issued.
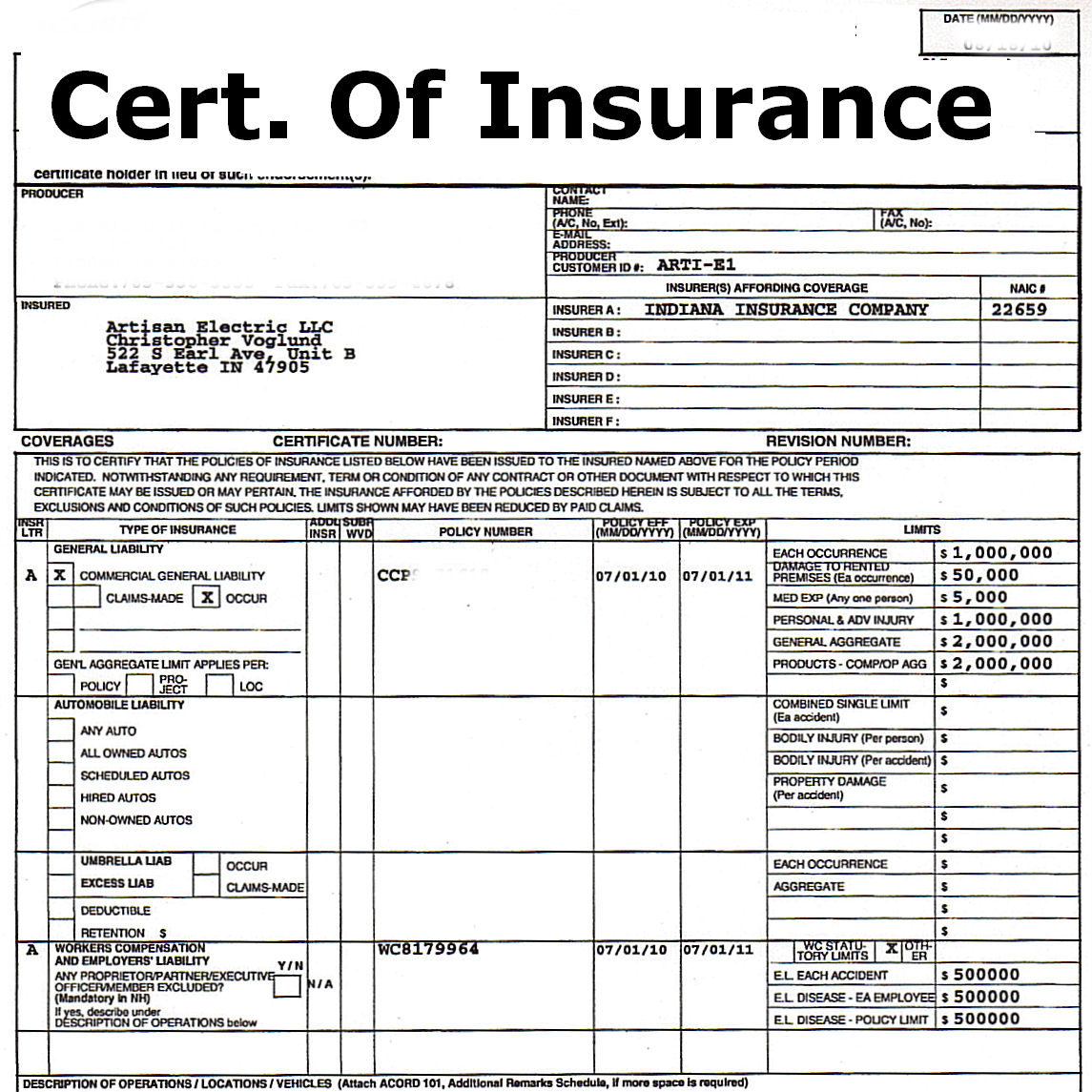
Sample Certificate of Insurance Template
Here is a sample certificate of insurance template with annotations to illustrate the key sections and information:
[Image of a sample certificate of insurance template with annotations]
Customization and Tailoring
Customizing certificate of insurance templates is crucial to meet specific business and insurance needs. Tailoring templates ensures they accurately reflect the coverage, limits, and policy details.
To tailor templates, consider the type of insurance policy, the business’s industry, and the specific requirements of the requesting party. For example, a contractor may need a template that includes liability coverage, while a healthcare provider may require a template that includes professional liability coverage.
Tips for Customizing Templates
- Review the insurance policy carefully to ensure the template accurately reflects the coverage and limits.
- Consider the specific needs of the business and the requesting party.
- Use clear and concise language to avoid confusion.
li>Proofread the template carefully before issuing it.
4. Design and Presentation
Professional design and presentation play a pivotal role in the effectiveness of certificates of insurance. They create a positive first impression, enhance readability, and convey the credibility and professionalism of the issuing organization.
When designing a certificate of insurance, it’s crucial to consider the following elements:
Font Selection
Select clear and legible fonts that are easy to read and understand. Avoid using fancy or decorative fonts that can be difficult to decipher. Stick to standard fonts like Arial, Calibri, or Times New Roman.
Color Scheme
Use a color scheme that is visually appealing and consistent with the organization’s branding. Avoid using too many colors or bright, distracting hues. Neutral colors like black, gray, and navy blue are often preferred for certificates of insurance.
Layout and Organization
The layout should be organized and logical, with clear sections for the policyholder, insurer, policy details, and other relevant information. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to structure the content effectively.
Well-Designed Certificate Example
A well-designed certificate of insurance features a clean and professional layout, uses clear and concise language, and employs a visually appealing color scheme. It should be easy to read and understand, providing all the necessary information in a clear and organized manner.
5. Distribution and Management
Distributing certificates of insurance is crucial for ensuring that all parties involved have the necessary documentation. There are various methods for distributing these certificates, including:
- Email: Sending certificates via email is a convenient and efficient method, allowing for quick and easy distribution to multiple recipients.
- Postal mail: While less common, postal mail can be used to distribute certificates in cases where email is not feasible.
- Online portals: Some insurance companies provide online portals where certificate holders can access and download their certificates directly.
Maintaining accurate records of issued certificates is essential for managing insurance coverage effectively. These records should include details such as the certificate number, the insured party, the coverage period, and the limits of liability. By maintaining accurate records, organizations can track the status of their insurance coverage and ensure that all certificates are up-to-date.
To manage certificates of insurance effectively, organizations can implement the following tips:
- Establish a central repository: Designate a specific location, either physical or digital, to store all certificates of insurance.
- Set up a system for tracking: Implement a system to track the status of each certificate, including its issuance date, expiration date, and any amendments made.
- Review certificates regularly: Regularly review certificates of insurance to ensure that they are up-to-date and reflect any changes in coverage.
Legal Considerations
Certificates of insurance carry significant legal implications, and understanding these is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. They serve as legal documents that attest to the existence and coverage details of insurance policies. Any inaccuracies or omissions within these certificates can lead to serious consequences.
Insurance companies are legally obligated to issue certificates of insurance that accurately reflect the terms and conditions of the underlying insurance policies. Providing false or incomplete information can constitute fraud and result in legal action against the insurance company. Similarly, individuals and businesses that knowingly accept or rely on inaccurate certificates may face legal repercussions.
Compliance with Laws and Regulations
Compliance with relevant laws and regulations governing certificates of insurance is essential to avoid legal risks. These laws vary by jurisdiction, and it is the responsibility of businesses and individuals to be aware of the applicable requirements in their respective locations. Some common laws and regulations include:
- Insurance regulations requiring insurance companies to issue certificates of insurance upon request.
- Laws prohibiting the alteration or falsification of certificates of insurance.
- Regulations governing the use of certificates of insurance as proof of insurance coverage.