General Overview of Fannie Mae Insurance Requirements
Fannie Mae insurance requirements play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and soundness of the mortgage market. Established by the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae), these requirements set forth the minimum insurance coverage that lenders must obtain to protect against financial losses resulting from defaults on mortgages that Fannie Mae purchases. By ensuring that mortgages meet specific insurance standards, Fannie Mae aims to mitigate risk and promote stability within the housing finance system.
Over the years, Fannie Mae insurance requirements have undergone several revisions to adapt to changing market conditions and regulatory mandates. These revisions have been driven by the need to address evolving risks, enhance consumer protections, and maintain the integrity of the mortgage-backed securities market. The current requirements represent a comprehensive framework that balances the need for adequate insurance coverage with the goal of fostering affordable and accessible mortgage lending.
Key Objectives and Goals of Fannie Mae’s Insurance Policies
Fannie Mae’s insurance policies are designed to achieve several key objectives, including:
- Protecting Fannie Mae from financial losses resulting from mortgage defaults.
- Ensuring that lenders have adequate coverage to meet their obligations to Fannie Mae.
- Mitigating the risk of mortgage fraud and other forms of financial abuse.
- Promoting confidence in the mortgage-backed securities market by providing investors with assurance that the underlying mortgages are adequately insured.
By achieving these objectives, Fannie Mae insurance requirements contribute to the stability and efficiency of the mortgage market, fostering a healthy environment for homeowners, lenders, and investors alike.
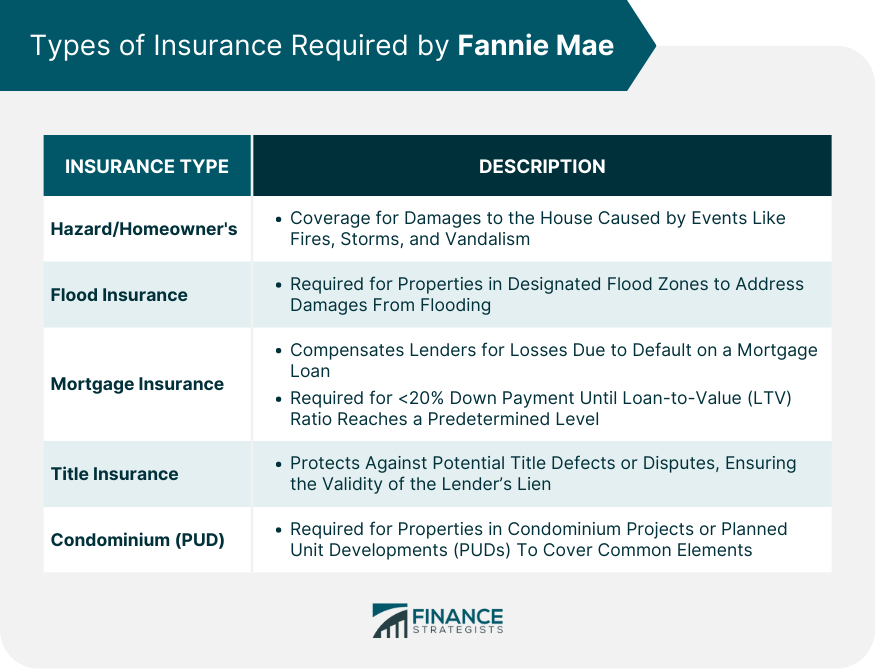
Types of Insurance Required by Fannie Mae
Fannie Mae requires various types of insurance to protect its mortgage investments and ensure that homeowners are adequately protected against financial losses. These insurance policies provide coverage for different risks associated with homeownership, ensuring that borrowers are financially secure in the event of unexpected events.
The primary types of insurance required by Fannie Mae include:
Homeowner’s Insurance
Homeowner’s insurance provides comprehensive coverage for the physical structure of the home, as well as its contents and personal belongings. It protects against losses due to fire, theft, vandalism, wind damage, and other covered perils. Fannie Mae requires borrowers to maintain homeowner’s insurance coverage equal to or greater than the replacement cost of the home.
Flood Insurance
Flood insurance is required for properties located in flood-prone areas. It provides coverage for damages caused by flooding, which is not typically covered under homeowner’s insurance. Fannie Mae requires flood insurance coverage equal to or greater than the amount of the mortgage loan.
Hazard Insurance
Hazard insurance provides coverage for damage to the home caused by specific hazards, such as earthquakes or windstorms. Fannie Mae requires hazard insurance coverage in areas where these hazards are prevalent. The coverage amount and deductibles may vary depending on the location and the specific hazards being insured against.
Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage insurance protects Fannie Mae in the event that a borrower defaults on their mortgage loan. It is typically required for borrowers who make a down payment of less than 20%. Mortgage insurance premiums are paid by the borrower and can be either a one-time upfront payment or an ongoing monthly premium.
These insurance policies work together to provide comprehensive protection for homeowners and Fannie Mae. They ensure that borrowers are financially secure in the event of unexpected events, and that Fannie Mae’s mortgage investments are protected against potential losses.
Eligibility Criteria for Fannie Mae Insurance
To obtain Fannie Mae insurance, borrowers must meet specific eligibility criteria established by the company. These criteria assess the borrower’s financial stability, property condition, and other factors to determine their eligibility for mortgage insurance.
Underwriting Process and Factors Considered
Fannie Mae’s underwriting process involves evaluating various factors to determine the borrower’s risk profile. These factors include:
- Credit history and score
- Debt-to-income ratio
- Loan-to-value ratio
- Property type and location
- Occupancy status
Documentation and Information Required
To apply for Fannie Mae insurance, borrowers must provide the following documentation and information:
- Mortgage application
- Credit report
- Income and asset statements
- Property appraisal
- Homeowners insurance policy
Costs and Premiums Associated with Fannie Mae Insurance
Fannie Mae insurance premiums are calculated based on several factors, including the loan amount, loan-to-value (LTV) ratio, credit score, and property type. The LTV ratio is the percentage of the loan amount to the appraised value of the property. A higher LTV ratio generally results in a higher premium. The credit score is a measure of the borrower’s creditworthiness. A higher credit score generally results in a lower premium. The property type is also a factor in determining the premium. For example, a single-family home will typically have a lower premium than a multi-family home.
In addition to the factors listed above, the premium may also be affected by the loan term and the type of insurance coverage. For example, a longer loan term will typically result in a higher premium. Similarly, a more comprehensive type of insurance coverage will typically result in a higher premium.
Fannie Mae insurance premiums are typically paid monthly or annually. The payment options and terms will vary depending on the lender. Some lenders may offer discounts for borrowers who pay their premiums annually.
Claims Process for Fannie Mae Insurance
The Fannie Mae claims process is designed to be efficient and straightforward. Here are the steps involved in filing a claim:
1. Report the Loss:
As soon as possible after discovering a covered loss, contact Fannie Mae or your mortgage servicer to report the claim. You will need to provide basic information about the loss, including the date, time, and location of the incident.
2. Submit a Claim Form:
You will need to complete a Fannie Mae insurance claim form and submit it to your mortgage servicer. The form will ask for detailed information about the loss, including the cause of damage, the extent of the damage, and the estimated cost of repairs.
3. Provide Supporting Documentation:
In addition to the claim form, you will need to provide supporting documentation to support your claim. This may include photographs of the damage, receipts for repairs, and estimates from contractors.
4. Claim Review and Approval:
Fannie Mae will review your claim and supporting documentation to determine if it is covered under your insurance policy. If the claim is approved, Fannie Mae will issue a payment to your mortgage servicer.
5. Payment of Claim:
Your mortgage servicer will apply the claim payment to your mortgage balance. If the claim payment is greater than the amount of your mortgage balance, you may receive a refund of the excess funds.
Exceptions and Exclusions to Fannie Mae Insurance Coverage
Fannie Mae insurance policies have certain exceptions and exclusions that limit the coverage provided. Understanding these limitations is crucial for homeowners to avoid any potential coverage gaps.
In general, Fannie Mae insurance policies do not cover losses or damages caused by:
Intentional Acts
- Acts of deliberate damage or destruction by the homeowner or anyone else with their permission.
- Damage caused by criminal acts, such as theft, vandalism, or arson.
Maintenance Neglect
- Losses resulting from a lack of proper maintenance or repairs.
- Damage caused by pests or rodents due to neglect.
Natural Disasters
- Coverage for natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, or hurricanes, is typically excluded unless the homeowner purchases additional coverage.
- However, Fannie Mae does offer a separate program called the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) for flood coverage.
Other Exclusions
- Losses due to war, terrorism, or nuclear events.
- Damage caused by faulty workmanship or materials.
- Losses incurred during the construction or renovation of the property.



