Definition of a Term Life Insurance Policy
A term life insurance policy is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specific period of time, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. If the insured person dies during the policy term, the death benefit is paid to the beneficiary. Term life insurance is typically less expensive than permanent life insurance, which provides coverage for the entire life of the insured person.
Key Features and Benefits
- Affordable: Term life insurance is typically more affordable than permanent life insurance, making it a good option for people on a budget.
- Flexibility: Term life insurance policies can be customized to meet the specific needs of the insured person. The policy term, death benefit, and premium payments can all be tailored to the individual’s situation.
- Simplicity: Term life insurance policies are relatively simple to understand. The coverage is straightforward, and there are no complex investment components.
Maturity of a Term Life Insurance Policy
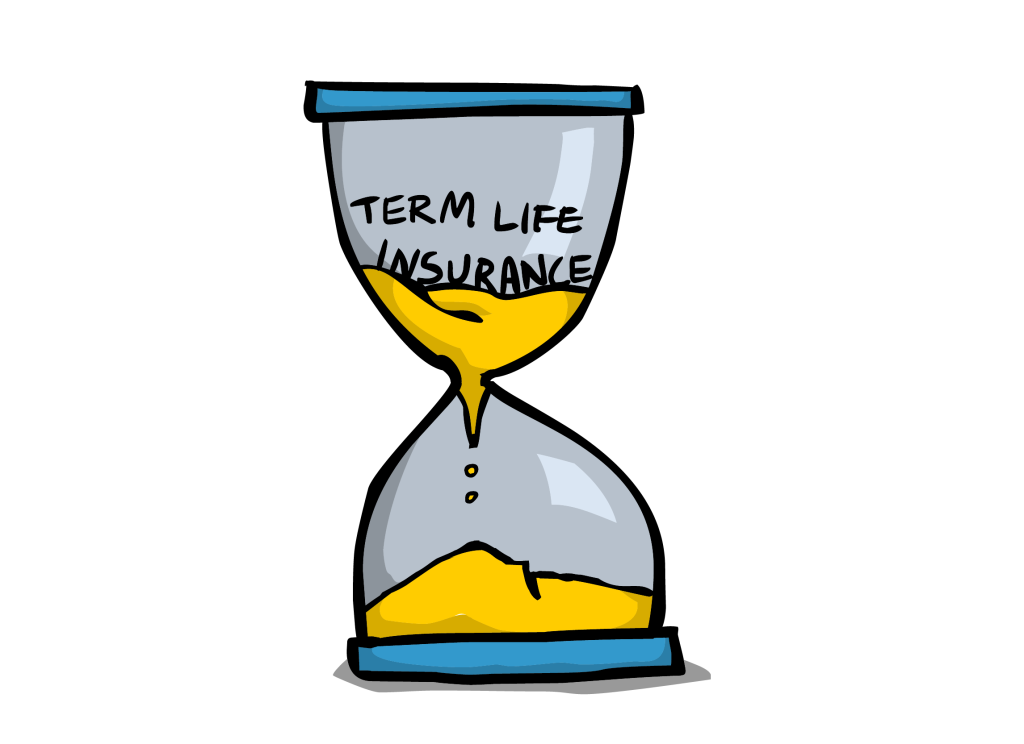
The maturity of a term life insurance policy refers to the point in time when the policy reaches its end date. Upon maturity, the policyholder has the option to renew the policy, let it expire, or convert it to a permanent life insurance policy.
A term life insurance policy matures when the insured person survives until the end of the policy term. The policy term is typically between 10 to 30 years. If the insured person dies during the policy term, the death benefit is paid to the beneficiary. However, if the insured person survives the policy term, the policy matures and the coverage ends.
Consequences of Policy Maturity
When a term life insurance policy matures, the policyholder has several options:
- Renew the policy: The policyholder can renew the policy for another term, usually at a higher premium rate.
- Let the policy expire: The policyholder can choose to let the policy expire, in which case there is no further coverage and no payout.
- Convert the policy to permanent life insurance: The policyholder can convert the term policy to a permanent life insurance policy, which provides lifelong coverage and a cash value component.
The decision of what to do when a term life insurance policy matures depends on the individual’s financial situation and insurance needs.
Payout and Beneficiaries of a Matured Term Life Insurance Policy
When a term life insurance policy matures, the insurance company pays out the death benefit to the designated beneficiaries. The payout amount is typically determined by the face amount of the policy, which is the amount of coverage purchased. Some policies may also include additional benefits, such as riders for accidental death or dismemberment.
The process of identifying and notifying beneficiaries begins when the policyholder passes away. The insurance company will typically contact the beneficiaries listed on the policy and provide them with information about the claim process. Beneficiaries will need to provide proof of identity and may also need to complete a claim form.
Once the claim has been processed, the insurance company will issue a check for the death benefit to the beneficiaries. Beneficiaries can use the funds to cover funeral expenses, pay off debts, or invest for the future.
Considerations for Choosing a Term Life Insurance Policy
When choosing a term life insurance policy, there are several factors to consider to ensure you select the best coverage for your needs.
Determining the Appropriate Term Length
Consider your financial obligations, such as mortgages, loans, and child-rearing expenses, to determine the length of coverage you need. Choose a term that aligns with your financial responsibilities and provides coverage until you no longer have dependents or financial burdens.
Determining the Amount of Coverage Needed
Calculate the amount of coverage needed to provide financial security for your beneficiaries in case of your untimely demise. Consider your income, debts, final expenses, and any potential future financial obligations. Aim to provide enough coverage to cover these expenses and maintain your family’s standard of living.
Understanding the Policy’s Terms and Conditions
Thoroughly read and understand the terms and conditions of the policy before purchasing. Pay attention to the coverage limits, exclusions, riders, and any specific requirements. Ensure you comprehend the policy’s provisions to avoid any surprises or misunderstandings in the future.
Comparison of Term Life Insurance Policies with Other Insurance Products
Term life insurance policies provide a straightforward and cost-effective way to protect loved ones financially in the event of an untimely death. However, it’s essential to understand how term life insurance compares to other insurance products to make an informed decision that aligns with individual needs and financial goals.
Term Life Insurance vs. Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers lifelong coverage and a cash value component that grows over time. In contrast, term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. While term life insurance premiums are generally lower than whole life insurance premiums, whole life insurance policies offer the advantage of building cash value, which can be borrowed against or withdrawn for various financial needs.
Term Life Insurance vs. Annuities
Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of income over a specific period or for the rest of one’s life. Unlike term life insurance, annuities do not provide a death benefit. However, they can be a valuable tool for retirement planning, as they offer a guaranteed income stream that can supplement Social Security benefits and other retirement savings.
Term Life Insurance in a Comprehensive Financial Plan
Term life insurance can be an essential component of a comprehensive financial plan. It provides financial protection for loved ones in the event of an untimely death, ensuring that they have the resources to maintain their standard of living and meet their financial obligations. Term life insurance can also be used to cover specific financial goals, such as paying for a child’s education or a mortgage.