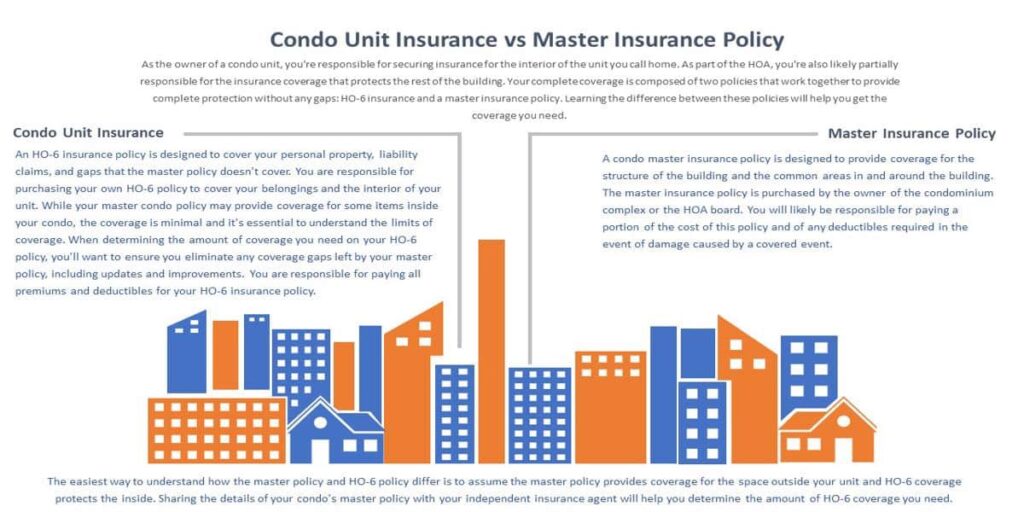
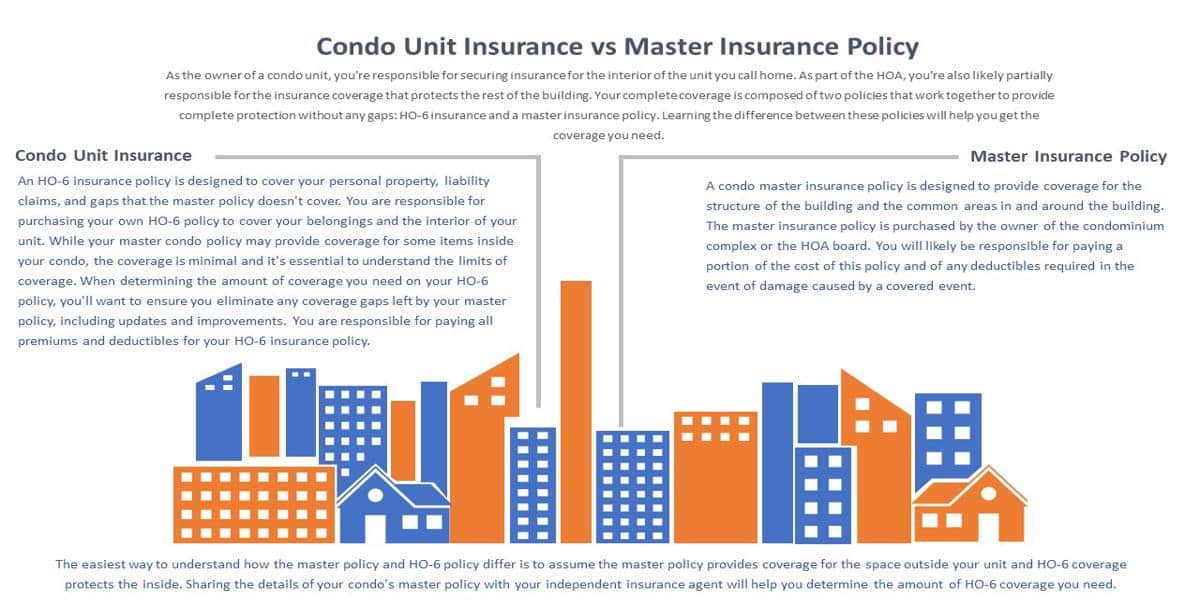
Types of Coverage
Condo master insurance policies typically provide a wide range of coverage options to protect the building and its common areas. These policies typically include:
- Building coverage: Protects the structure of the building, including walls, roof, and foundation, from damage caused by covered perils.
- Common area coverage: Protects the common areas of the building, such as lobbies, hallways, and elevators, from damage caused by covered perils.
- Liability coverage: Protects the condo association from lawsuits alleging bodily injury or property damage caused by the building or its common areas.
- Loss assessment coverage: Protects the condo association from financial assessments levied to cover the cost of repairs or replacements to the building or its common areas.
Covered Perils
Common covered perils in condo master insurance policies include:
- Fire
- Windstorm
- Hail
- Lightning
- Theft
- Vandalism
- Water damage
Exclusions
Some common exclusions in condo master insurance policies include:
- Earthquakes
- Floods
- Acts of war
- Intentional damage
- Wear and tear
Coverage Limits
Understanding coverage limits is crucial when it comes to condo master insurance. These limits define the maximum amount of financial protection provided by the policy, and they directly impact the extent of coverage you have for various aspects of your condo building.
Determining appropriate coverage limits requires careful consideration of the specific risks and vulnerabilities of your building. This involves assessing factors such as the building’s size, construction materials, age, and location.
Property Damage
Property damage coverage limits determine the maximum amount the insurance will pay to repair or replace the building and its contents in the event of a covered loss, such as fire, windstorm, or vandalism.
Liability
Liability coverage limits protect the condo association and its members from financial responsibility in the event of bodily injury or property damage caused to others as a result of the condo building or its operations.
Loss of Rents
Loss of rents coverage provides financial protection to the condo association in the event that the building becomes uninhabitable due to a covered loss, resulting in a loss of rental income.
Deductibles and Premiums
Deductibles and premiums are essential components of condo master insurance policies. Understanding how they work and their impact on coverage costs is crucial.
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before the insurance policy starts to cover claims. Higher deductibles typically result in lower premiums. Conversely, lower deductibles mean higher premiums.
Premium Calculation
Premiums are the annual fees you pay to maintain your insurance coverage. They are calculated based on several factors, including the following:
- Deductible amount
- Coverage limits
- Property location
- Claims history
- Building type and age
By carefully considering your deductible and premium options, you can tailor your condo master insurance policy to meet your specific needs and budget.
Claim Process
Filing and processing a claim under a condo master insurance policy involves several steps:
– Notifying the insurance company: Promptly report the loss or damage to the insurance company. Provide details such as the date, time, location, and cause of the incident.
– Documenting the loss: Take photos or videos of the damaged property, and gather any relevant documentation, such as receipts for repairs or estimates.
– Submitting a claim form: Fill out the claim form provided by the insurance company and submit it along with the supporting documentation.
– Investigation: The insurance company may send an adjuster to inspect the damage and assess the claim.
– Settlement: Once the investigation is complete, the insurance company will determine the amount of coverage available and issue a settlement payment.
Tips for Maximizing Claim Settlement
– Be accurate and detailed: Provide clear and complete information about the loss or damage.
– Document everything: Take photos, gather receipts, and keep a record of all communications with the insurance company.
– Cooperate with the adjuster: Provide the adjuster with access to the damaged property and any requested information.
– Review the settlement offer carefully: Ensure that the settlement amount covers the actual cost of repairs or replacement.
– Consider getting a second opinion: If you disagree with the insurance company’s settlement offer, consider getting an independent appraisal or estimate.
Shared Responsibilities
Condo insurance coverage is a shared responsibility between the condo association and individual unit owners. The association typically maintains a master policy that covers common areas and shared amenities, while unit owners are responsible for insuring their own units and personal belongings.
Clear communication and coordination are crucial to ensure adequate protection for all parties involved. The condo association should provide unit owners with a detailed explanation of the master policy, including coverage limits and exclusions. Unit owners should review their own policies carefully and ensure that they have sufficient coverage to protect their personal assets.
- The condo association is responsible for maintaining insurance coverage for common areas and shared amenities, such as the lobby, elevators, hallways, and swimming pool.
- Individual unit owners are responsible for insuring their own units, including the interior structure, fixtures, and personal belongings.
- Both the condo association and individual unit owners should work together to ensure that there is no gap in coverage.
Special Considerations
Condo master insurance coverage may require special considerations for certain unique or specialized circumstances. These include high-rise buildings, mixed-use properties, and historic buildings.
High-rise buildings present unique challenges, such as increased risk of fire, wind damage, and water leaks. Mixed-use properties require coverage that addresses both residential and commercial uses. Historic buildings may have special requirements to maintain their architectural integrity.
High-Rise Buildings
High-rise buildings require specialized coverage due to their increased exposure to certain risks. These risks include:
- Fire: High-rise buildings are more susceptible to fire due to their height and the presence of multiple floors and units.
- Wind damage: High winds can cause significant damage to high-rise buildings, particularly to exterior walls and windows.
- Water leaks: High-rise buildings are more prone to water leaks due to the complex plumbing systems and the potential for roof damage.
Mixed-Use Properties
Mixed-use properties present unique challenges for insurance coverage. These properties typically include both residential and commercial units, each with its own unique set of risks. The insurance policy must address the needs of both types of units.
For example, the policy should cover the following:
- Residential units: Coverage for personal property, liability, and loss of use.
- Commercial units: Coverage for business property, liability, and business interruption.
Historic Buildings
Historic buildings require special coverage to protect their architectural integrity. The policy should include the following:
- Coverage for the cost of repairing or replacing damaged or destroyed historic features.
- Coverage for the cost of restoring the building to its original condition.
- Coverage for the cost of protecting the building from further damage during the repair process.
Tips for Condo Owners
Understanding your condo master insurance coverage is crucial to ensure your unit and belongings are adequately protected. Here are some practical tips to help you navigate your policy and make informed decisions:
Review your policy carefully: Understand the coverage provided, limits, and exclusions. Make sure you’re aware of what’s covered and what’s not. Contact your insurance agent or the condo association if you have any questions.
Communicate with the condo association: The condo association typically manages the master insurance policy. Stay informed about any changes or updates to the policy and communicate your concerns or questions to the association.
Make informed decisions about coverage: Consider your individual needs and circumstances when reviewing your coverage. You may need additional coverage for personal belongings or specific risks not covered by the master policy.
Understanding Coverage
Condo master insurance typically includes the following coverage:
- Building structure: Coverage for the building’s exterior and common areas.
- Personal property: Coverage for your personal belongings within your unit.
- Liability: Coverage for accidents or injuries that occur within your unit.
- Loss assessment: Coverage for assessments levied by the condo association to repair or replace common areas.
Determining Coverage Limits
Coverage limits vary depending on the policy. Ensure you have adequate coverage for your personal property and liability.
Personal property: Consider the value of your belongings and select a coverage limit that covers their replacement cost.
Liability: Choose a liability limit that provides sufficient protection against potential claims.
Choosing Deductibles
Deductibles are the amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles generally result in lower premiums.
Consider your financial situation and risk tolerance when selecting a deductible. A higher deductible can save you money on premiums, but it also means you’ll have to pay more out-of-pocket if you file a claim.
Filing Claims
If you need to file a claim, promptly notify the condo association and your insurance company. Provide detailed documentation and evidence to support your claim.
Stay organized and keep records of all communication and expenses related to the claim.