Employer Responsibilities
Upon qualifying for long-term disability benefits, employees can typically expect their employer-provided health insurance coverage to continue for a specific period.
The duration of this coverage varies depending on factors such as company size, industry, and state regulations. In general, larger companies tend to offer more generous coverage periods, while smaller companies may have shorter coverage durations.
Coverage Period
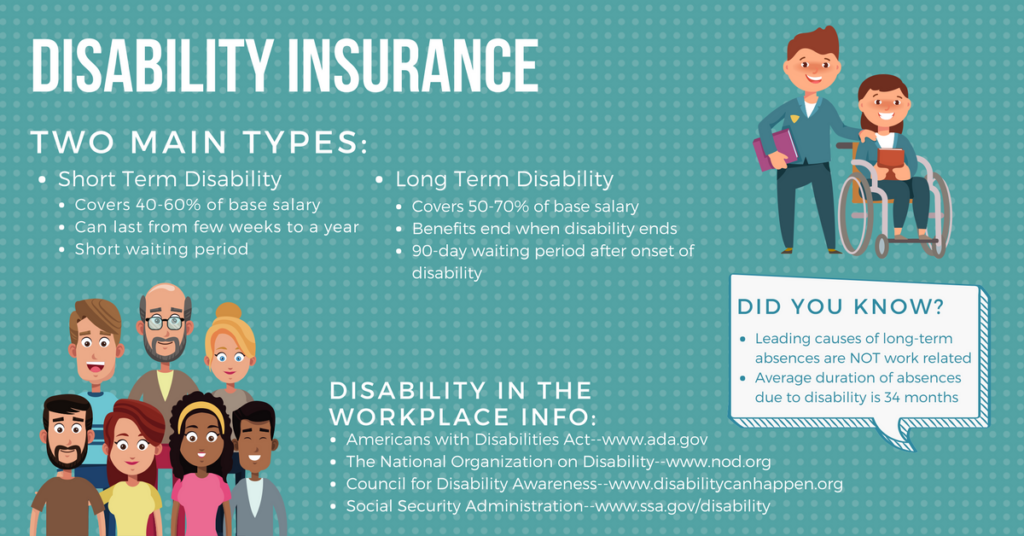
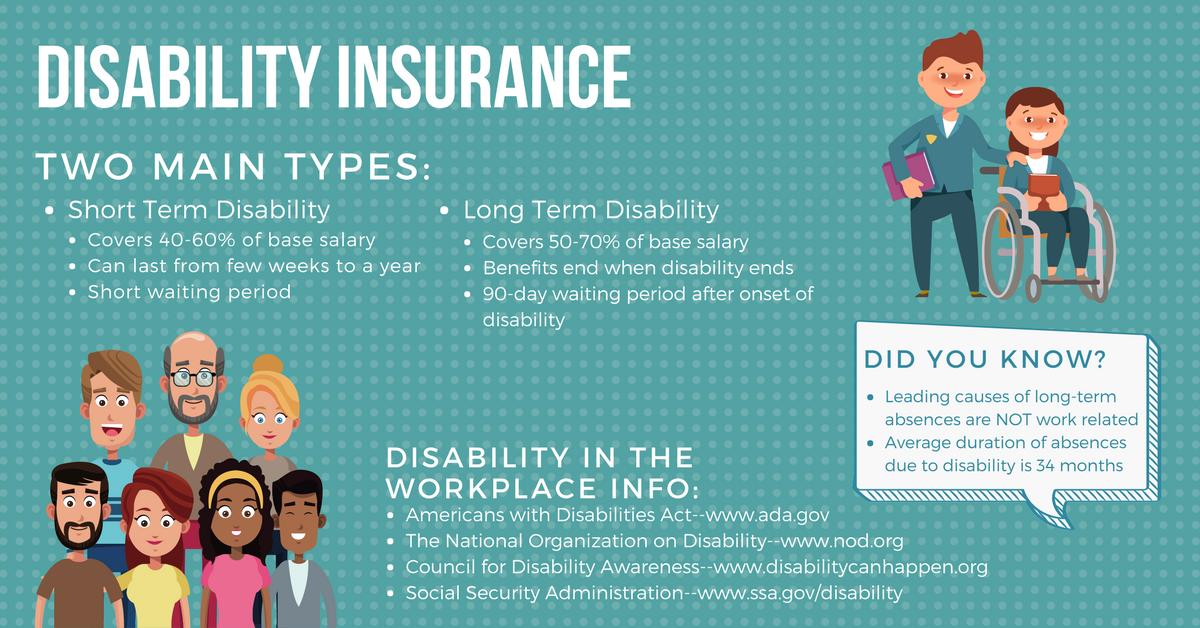
- Small employers (less than 50 employees): Typically provide coverage for 12 to 24 months.
- Medium-sized employers (50 to 499 employees): Often extend coverage for 18 to 36 months.
- Large employers (500 or more employees): May offer coverage for 36 months or longer.
Employer Contributions and Employee Premiums
During the coverage period, employers may continue to contribute towards the employee’s health insurance premiums, either in full or partially. The employee may also be responsible for paying a portion of the premiums, depending on the company’s policy.
For example, an employer may contribute 75% of the health insurance premiums while the employee pays the remaining 25%.
Employee Responsibilities
During long-term disability, employees typically share some financial responsibility for their health insurance premiums.
Premium Payments
Employees may be required to pay a portion of their health insurance premiums while on long-term disability. The specific amount will vary depending on the employer’s plan and the employee’s coverage level.
Grace Periods and Assistance Programs
Some employers offer grace periods during which employees do not have to pay their premiums. Additionally, some employers may have premium assistance programs that help employees with the cost of their premiums.
COBRA Coverage
If an employee is not eligible for employer-sponsored health insurance while on long-term disability, they may be eligible for COBRA coverage. COBRA is a federal law that allows employees to continue their health insurance coverage at their own expense.
Government Programs
Government programs offer health insurance coverage for individuals on long-term disability. These programs include Medicare, Medicaid, and the Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) program.
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for people 65 or older, younger people with certain disabilities, and people with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance) can provide coverage for hospital stays, doctor visits, and other medical expenses.
Medicaid is a state and federal health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. Medicaid coverage varies by state, but it typically includes hospital stays, doctor visits, prescription drugs, and other medical expenses.
SSDI is a federal disability insurance program that provides monthly benefits to people who are unable to work due to a disability. SSDI recipients are eligible for Medicare after a 24-month waiting period.
Government programs can interact with employer-provided health insurance coverage in several ways. For example, if an individual is eligible for both Medicare and employer-provided health insurance, they may be able to coordinate their benefits to maximize their coverage. Additionally, if an individual loses their employer-provided health insurance due to a disability, they may be able to qualify for Medicaid or Medicare.
Long-Term Disability Insurance Policies
Long-term disability insurance (LTD) policies can provide valuable coverage for health insurance costs while you are unable to work due to a disability. These policies typically cover a portion of your income and may also include coverage for health insurance premiums.
The definition of disability and the benefit period are two important factors that impact coverage. The definition of disability determines whether you are eligible for benefits, and the benefit period determines how long you can receive benefits.
When selecting an LTD policy, it is important to consider your individual needs and financial situation. You should also make sure that the policy includes coverage for health insurance premiums.