Definition of Evidence of Insurability
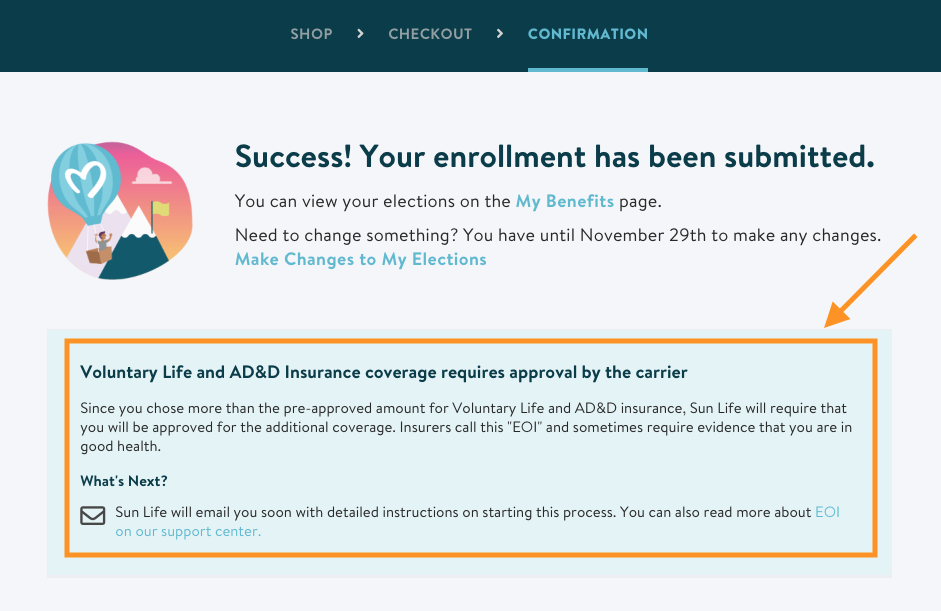
Evidence of insurability refers to the information and documentation that an individual or business provides to an insurance company to demonstrate their insurability. It helps the insurance company assess the risk associated with providing insurance coverage and determine appropriate premium rates.
The purpose of evidence of insurability is to provide the insurance company with a clear understanding of the applicant’s health, lifestyle, financial situation, and other relevant factors that may impact the likelihood of a claim. This information enables the insurer to make informed decisions about the level of coverage, premium rates, and any exclusions or limitations that may apply.
Types of Evidence of Insurability
Evidence of insurability is categorized into two main types: underwriting and non-underwriting evidence.
Underwriting Evidence
Underwriting evidence is used by insurance companies to assess the risk of insuring an individual or business. This type of evidence includes:
- Medical history: This includes information about the individual’s past and present health conditions, as well as any medications they are taking.
- Lifestyle information: This includes information about the individual’s smoking habits, alcohol consumption, and exercise routine.
- Occupation: This includes information about the individual’s job title and industry, as well as any potential hazards associated with their work.
- Driving record: This includes information about the individual’s driving history, including any accidents or traffic violations.
- Financial history: This includes information about the individual’s income, assets, and debts.
Non-Underwriting Evidence
Non-underwriting evidence is used by insurance companies to verify the identity of the individual or business being insured. This type of evidence includes:
- Government-issued identification: This includes a driver’s license, passport, or national ID card.
- Proof of address: This includes a utility bill, lease agreement, or mortgage statement.
- Employment verification: This includes a letter from the individual’s employer.
- Bank statements: These can be used to verify the individual’s income and assets.
Methods for Verifying Evidence of Insurability
Verifying evidence of insurability is a crucial step in the underwriting process, ensuring that the insurer has a clear understanding of the applicant’s risk profile and that the coverage provided is appropriate. Several methods are commonly employed to verify the authenticity and accuracy of evidence submitted by applicants.
These methods vary in their level of invasiveness and the information they provide. The choice of method depends on factors such as the type of insurance being applied for, the applicant’s risk profile, and the insurer’s underwriting guidelines.
Medical Examination
A medical examination is a comprehensive physical examination performed by a licensed physician. It typically involves a review of the applicant’s medical history, a physical examination, and laboratory tests. The purpose of a medical examination is to assess the applicant’s overall health status, identify any potential health risks, and determine the applicant’s insurability.
Advantages: Provides a thorough assessment of the applicant’s health status, reducing the risk of adverse selection for the insurer.
Limitations: Can be invasive and time-consuming, and may not always detect all health conditions.
Medical Records Review
A medical records review involves obtaining and reviewing the applicant’s medical records from their healthcare providers. This review can provide valuable insights into the applicant’s medical history, including diagnoses, treatments, and medications. It can also help identify any gaps in the applicant’s medical care.
Advantages: Provides a comprehensive view of the applicant’s medical history, reducing the risk of adverse selection.
Limitations: May not be available for all applicants, and may not always provide a complete picture of the applicant’s health status.
Interview
An interview with the applicant can provide valuable information about their lifestyle, habits, and family medical history. The interviewer can ask specific questions about the applicant’s health, occupation, and hobbies to assess their risk profile.
Advantages: Allows the insurer to gather information directly from the applicant, reducing the risk of misrepresentation.
Limitations: May be subjective and rely on the applicant’s honesty and accuracy.
Third-Party Verification
Third-party verification involves contacting the applicant’s healthcare providers, employers, or other relevant sources to confirm the information provided in the application. This can help verify the applicant’s medical history, income, and other relevant details.
Advantages: Provides independent verification of the applicant’s information, reducing the risk of fraud.
Limitations: Can be time-consuming and may not always be possible to obtain all necessary information.
Importance of Accurate Evidence of Insurability
Providing accurate and complete evidence of insurability is crucial for several reasons. It ensures that the insurance company has a clear understanding of the applicant’s risk profile, which helps in determining the appropriate premium and coverage terms.
Inaccurate or incomplete evidence can lead to underwriting errors, resulting in either over- or under-insurance. Over-insurance can result in unnecessary premium payments, while under-insurance may leave the policyholder financially exposed in the event of a claim.
Consequences of Inaccurate or Incomplete Evidence
- Delayed or denied claims: If the evidence provided does not accurately reflect the applicant’s risk, the insurance company may delay or deny claims, arguing that the policyholder misrepresented their insurability.
- Higher premiums: Inaccurate evidence may lead to the insurance company assessing a higher premium, as they may perceive the applicant as a higher risk than they actually are.
- Loss of coverage: If the insurance company discovers that the evidence provided was intentionally misleading, they may cancel the policy, leaving the policyholder without coverage.
5. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Evidence of insurability is subject to legal and ethical considerations that insurers and policyholders must adhere to. Understanding these considerations is crucial to maintain trust and fairness in the insurance industry.
Obligations and Responsibilities
- Insurers have a legal obligation to underwrite policies fairly and accurately, considering the evidence of insurability provided by the applicant.
- Policyholders have a duty to provide complete and truthful information about their insurability factors.
Implications of Withholding or Falsifying Evidence
Withholding or falsifying evidence of insurability can have severe consequences:
- For insurers, it can lead to financial losses and reputational damage.
- For policyholders, it can result in denied claims, policy cancellations, or increased premiums.
Ethical Considerations
Beyond legal obligations, insurers and policyholders have ethical responsibilities to act in good faith. This includes:
- Protecting the privacy and confidentiality of applicants’ information.
- Treating all applicants fairly and without discrimination.
- Encouraging transparency and honesty throughout the insurance process.