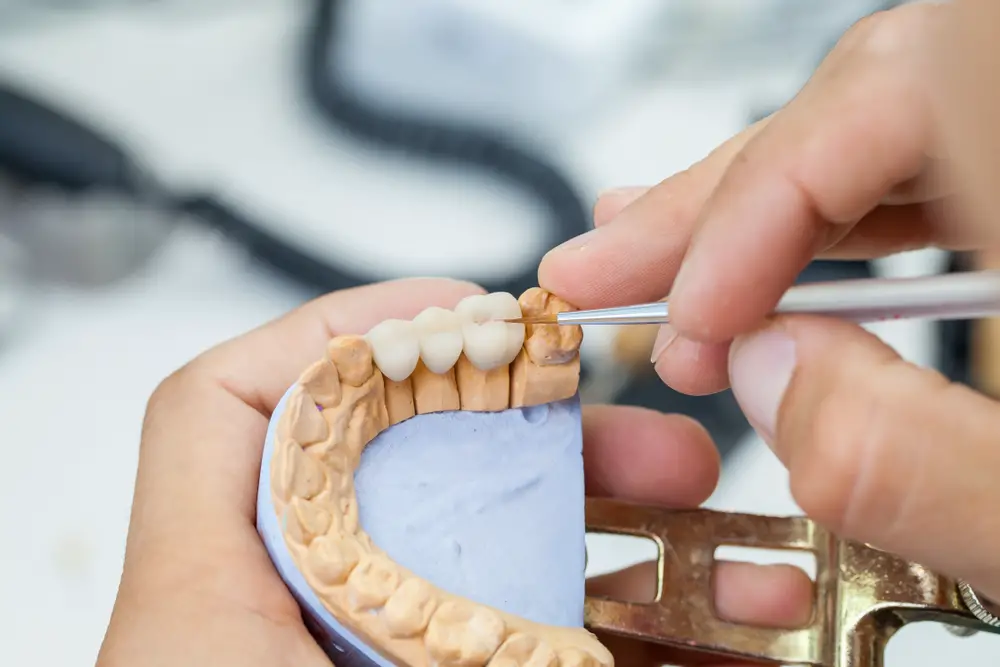
Materials and Fabrication Costs
The materials used in dental bridges and the fabrication process significantly impact their overall cost. Let’s delve into the details:
Materials
Dental bridges can be made from various materials, each with its own cost implications:
- Gold: Gold is a durable and biocompatible material, but it is also the most expensive option.
- Porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM): PFM bridges combine the strength of metal with the aesthetics of porcelain, making them a popular choice. However, they are more expensive than all-metal bridges.
- All-ceramic: All-ceramic bridges provide excellent aesthetics and durability, but they can be more fragile and expensive than PFM bridges.
- Zirconia: Zirconia is a strong and durable material that is also aesthetically pleasing. It is a cost-effective alternative to porcelain-fused-to-metal bridges.
Fabrication Process
The fabrication process also affects the cost of a dental bridge. It involves several steps:
- Impressions: Dental impressions are taken to create a mold of the patient’s teeth and jaw.
- Wax-up: A wax model of the bridge is created based on the impressions.
- Casting: The wax model is used to create a metal or ceramic framework for the bridge.
- Bonding: The framework is bonded to the abutment teeth using dental cement.
The complexity of the fabrication process and the materials used determine the time and labor required, which ultimately influence the overall cost of the dental bridge.
Dental Professional Fees
Dental professional fees associated with dental bridge placement involve the consultation, examination, and the actual bridge placement procedure. These fees vary depending on factors such as the experience and location of the dentist.
During the initial consultation, the dentist will examine your teeth and discuss your treatment options. The dentist will also take X-rays to assess the condition of your teeth and jawbone. The cost of the consultation will vary depending on the dentist’s fees and the complexity of your case.
Examination Fees
Examination fees cover the dentist’s time and expertise in assessing the condition of your teeth and jawbone. The cost of an examination will vary depending on the dentist’s fees and the complexity of your case.
Bridge Placement Fees
Bridge placement fees cover the dentist’s time and expertise in placing the dental bridge. The cost of bridge placement will vary depending on the type of bridge, the number of teeth involved, and the complexity of the procedure.
Lab Fees
The dental laboratory plays a crucial role in fabricating the dental bridge. Their fees cover the materials, labor, and equipment used to create the prosthesis.
Several factors influence lab fees, including:
Materials
- Type of material used for the bridge (e.g., porcelain, zirconia, gold)
- Quality and durability of the material
- Quantity of material required
Complexity
- Design and shape of the bridge
- Number of units (teeth) involved
- Presence of any additional features (e.g., pontics, abutments)
Turnaround Time
- Standard turnaround time (usually 2-3 weeks)
- Expedited turnaround time (additional fees may apply)
- Emergency turnaround time (significant additional fees)
Additional Expenses
In addition to the primary costs associated with a dental bridge, there are potential additional expenses that may arise during the procedure.
These expenses can vary depending on the complexity of the case, the location of the dental practice, and the materials used.
Consultation and Examination
Before the dental bridge procedure, a consultation and examination are typically required to assess the patient’s oral health and determine the best course of treatment.
This may include X-rays, impressions, and other diagnostic tests to evaluate the condition of the teeth and jawbone.
Insurance Considerations
Dental insurance can significantly impact the cost of a dental bridge. Many insurance plans cover a portion of the costs associated with dental bridges, including materials, fabrication, and professional fees. However, it is important to understand the limitations and exclusions that may apply to your specific insurance coverage.
Coverage Limitations
Dental insurance policies typically have annual maximums, which limit the total amount of coverage you can receive in a given year. Additionally, some plans may have waiting periods before certain procedures, such as dental bridges, are covered. It is essential to check with your insurance provider to determine your specific coverage details.
Exclusions
Certain factors may exclude dental bridges from insurance coverage. These exclusions can include:
- Pre-existing conditions: If you had dental problems before your insurance coverage began, they may not be covered.
- Cosmetic procedures: Dental bridges that are primarily for cosmetic purposes may not be covered.
- Negligence: If the need for a dental bridge is due to negligence or lack of proper dental care, it may not be covered.
Financing Options
For individuals who cannot afford the full cost of a dental bridge upfront, there are several financing options available to help make the procedure more accessible.
Each financing option comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. It is important to carefully consider these factors before making a decision.
Loans
- Advantages: Loans typically offer lower interest rates than credit cards and can be tailored to meet your specific financial needs.
- Disadvantages: Loans may require a credit check and can have strict repayment terms.
Credit Cards
- Advantages: Credit cards are widely accepted and offer convenience. Some cards may also offer rewards or cash back.
- Disadvantages: Credit cards typically have higher interest rates than loans and can be difficult to manage if you carry a balance.
Dental Financing Plans
- Advantages: Dental financing plans are specifically designed for dental procedures and often offer low interest rates and flexible repayment terms.
- Disadvantages: Dental financing plans may have application fees and can be limited to certain dental providers.
Payment Plans
- Advantages: Payment plans allow you to spread the cost of your dental bridge over a period of time, typically with no interest.
- Disadvantages: Payment plans may require a down payment and can have strict payment deadlines.
Cost Comparison
When comparing the costs of different dental bridges, several factors come into play, including the materials used, the fabrication method, and any additional expenses.
The following table provides an overview of the average costs associated with different types of dental bridges:
Materials
- Porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM): This type of bridge is made of a metal framework that is covered with porcelain. PFM bridges are strong and durable, and they can be matched to the color of your natural teeth.
- All-ceramic: These bridges are made entirely of ceramic, which makes them more aesthetically pleasing than PFM bridges. However, all-ceramic bridges are also more fragile.
- Zirconia: Zirconia bridges are made of a strong, white material that is similar to porcelain. Zirconia bridges are very durable and can be used to replace multiple missing teeth.
Fabrication Method
- Traditional: Traditional bridges are made by taking impressions of your teeth and sending them to a dental lab. The lab will then create a metal framework that is fitted to your teeth. The porcelain is then applied to the framework and baked in an oven.
- CAD/CAM: CAD/CAM (computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing) bridges are made using a digital scanner to create a 3D model of your teeth. The model is then used to create a wax pattern, which is then cast in metal. The porcelain is then applied to the metal framework and baked in an oven.
Additional Expenses
- Consultation fee: You will need to pay a consultation fee to see a dentist and discuss your treatment options.
- X-rays: You will need to have X-rays taken of your teeth so that the dentist can assess your oral health.
- Anesthesia: You may need to be given anesthesia during the procedure, which will add to the cost.
- Follow-up appointments: You will need to have follow-up appointments with your dentist to check on the progress of your healing.
Case Studies
Real-life examples can help provide insights into the costs and decision-making processes involved in getting a dental bridge without insurance. Here are a few case studies:
Case Study 1
A 45-year-old woman with a missing molar opted for a three-unit porcelain-fused-to-metal bridge. The cost of the procedure, including materials, fabrication, dental fees, and lab fees, amounted to approximately $3,500. She decided to proceed with the bridge to restore her chewing function and improve her smile’s aesthetics.
Case Study 2
A 60-year-old man needed to replace a missing premolar. He chose a two-unit zirconia bridge, which cost him around $2,800. The decision was influenced by the bridge’s durability, natural appearance, and the fact that it did not require any metal components.
These case studies demonstrate the variability in costs and factors that can influence a patient’s decision when getting a dental bridge without insurance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cost of a dental bridge without insurance varies significantly depending on the factors discussed above. To save money on your dental bridge procedure, consider getting quotes from multiple dentists, negotiating a payment plan, and looking into dental savings plans or dental schools that offer reduced-cost services.
Tips for Saving Money on Dental Bridge Procedure
- Get quotes from multiple dentists.
- Negotiate a payment plan with your dentist.
- Look into dental savings plans.
- Consider getting your dental bridge done at a dental school.