Cost of Fillings Without Insurance
The cost of fillings without insurance can vary depending on several factors, including the type of filling material used, the location of the cavity, and the complexity of the procedure. On average, the cost of a filling without insurance can range from $100 to $500 or more.
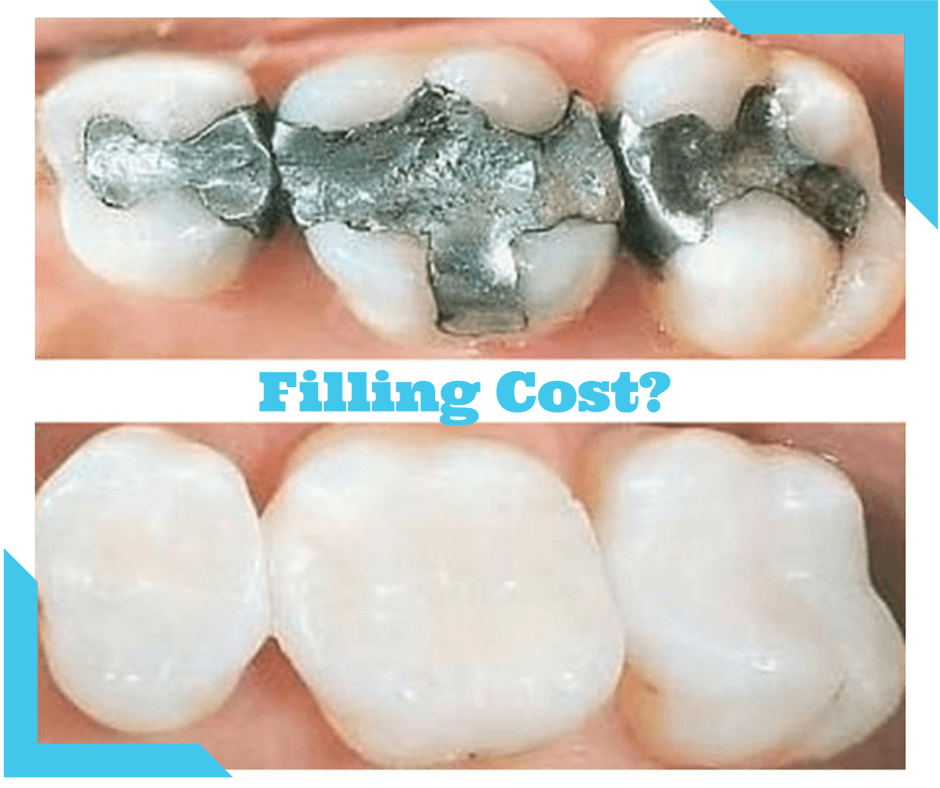
The type of filling material used is one of the primary factors that influence the cost of a filling. Amalgam fillings, which are made of a combination of metals, are typically the most affordable option, with an average cost of around $100 to $200. Composite fillings, which are made of a resin material, are more aesthetically pleasing and durable than amalgam fillings, but they are also more expensive, with an average cost of around $200 to $400. Gold fillings are the most expensive type of filling, with an average cost of around $400 to $500 or more.
The location of the cavity can also affect the cost of a filling. Fillings in molars, which are located at the back of the mouth, are typically more expensive than fillings in front teeth, as they require more material and are more difficult to access.
The complexity of the procedure can also affect the cost of a filling. If the cavity is large or deep, it may require a more complex procedure, which can increase the cost of the filling.
Types of Filling Materials
Fillings are used to restore damaged teeth. There are different types of filling materials available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common type of filling material is amalgam. Amalgam is a mixture of metals, including silver, tin, copper, and mercury. Amalgam fillings are strong and durable, and they are relatively inexpensive. However, amalgam fillings are also noticeable because of their silver color.
Composite resin fillings are another common type of filling material. Composite resin is a tooth-colored material that is made of a mixture of plastic and glass. Composite resin fillings are strong and durable, and they are less noticeable than amalgam fillings. However, composite resin fillings are more expensive than amalgam fillings.
Glass ionomer fillings are a type of filling material that is made of a mixture of glass and acrylic. Glass ionomer fillings are strong and durable, and they release fluoride, which helps to prevent tooth decay. However, glass ionomer fillings are not as strong as amalgam or composite resin fillings, and they are more likely to chip or break.
Ceramic fillings are a type of filling material that is made of porcelain. Ceramic fillings are strong and durable, and they are very natural-looking. However, ceramic fillings are more expensive than amalgam or composite resin fillings.
The best type of filling material for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences. Your dentist can help you choose the right type of filling material for your situation.
Amalgam Fillings
Amalgam fillings are the most common type of filling material. They are made of a mixture of metals, including silver, tin, copper, and mercury. Amalgam fillings are strong and durable, and they are relatively inexpensive. However, amalgam fillings are also noticeable because of their silver color.
Advantages of amalgam fillings:
- Strong and durable
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages of amalgam fillings:
- Noticeable because of their silver color
- May contain mercury
Procedure for Getting a Filling
Getting a filling is a common dental procedure used to repair decayed or damaged teeth. The process involves several steps:
1. Initial Consultation: You will consult with your dentist to discuss your symptoms, examine the affected tooth, and determine if a filling is necessary.
2. Preparation: Before placing the filling, the dentist will numb the area around the tooth using local anesthesia. This injection helps minimize any discomfort during the procedure.
3. Removal of Decay: The dentist will use a drill or laser to remove the decayed or damaged portion of the tooth. This step helps create a clean surface for the filling to adhere to.
4. Filling Placement: The dentist will select a suitable filling material based on the size and location of the cavity. The material is applied to the prepared tooth and shaped to restore the tooth’s form and function.
5. Hardening: If a composite filling is used, it will be hardened using a curing light. For other materials, such as amalgam, a chemical reaction occurs to harden the filling.
6. Polishing: Once the filling has hardened, the dentist will smooth and polish it to ensure a comfortable fit and prevent irritation to the surrounding tissues.
Maintenance and Longevity of Fillings
To preserve the longevity of your fillings, meticulous care is essential. By following a diligent maintenance routine and attending regular dental appointments, you can effectively prolong the lifespan of your fillings.
Regular dental checkups and cleanings play a pivotal role in maintaining the health of your teeth and fillings. During these appointments, your dentist will meticulously examine your fillings, identify any signs of wear or damage, and promptly address any issues to prevent further deterioration.
Tips for Maintaining Fillings
- Practice meticulous oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing at least once a day. This diligent regimen removes plaque and bacteria, safeguarding your fillings from decay and deterioration.
- Avoid consuming foods and beverages that can damage your fillings, such as hard candies, ice, and sugary drinks. These substances can exert excessive pressure on your fillings, potentially causing them to crack or dislodge.
- If you participate in contact sports or engage in activities that may impact your teeth, consider wearing a mouthguard to protect your fillings from damage.
- Refrain from using your teeth as tools to open packages or bite down on hard objects. These actions can subject your fillings to undue stress, increasing the risk of fractures or other damage.
Alternatives to Fillings
Apart from fillings, other treatment options are available to address cavities. These alternatives vary in terms of their materials, procedures, and cost. Understanding the pros and cons of each option can help you make an informed decision.
Dental crowns, inlays, and onlays are common alternatives to fillings. Each option offers unique advantages and drawbacks, which will be explored in the following sections.
Dental Crowns
Dental crowns are tooth-shaped caps that cover the entire visible portion of a tooth. They are typically made of porcelain, metal, or a combination of both materials. Crowns are used to restore the strength and appearance of a severely damaged or decayed tooth.
Pros:
- Provides full coverage and protection for the tooth.
- Restores the tooth’s original shape and appearance.
- Durable and long-lasting.
Cons:
- Requires extensive tooth preparation, which involves removing a significant amount of tooth structure.
- Can be more expensive than fillings.
- May require replacement over time.
Inlays and Onlays
Inlays and onlays are partial crowns that cover only the damaged or decayed portion of a tooth. They are custom-made to fit the tooth precisely and are typically made of porcelain or composite resin.
Pros:
- Preserves more of the natural tooth structure compared to crowns.
- Can be less expensive than crowns.
- Can be matched to the color of the natural teeth for a more aesthetic result.
Cons:
- May not be suitable for teeth with extensive damage or decay.
- Can be more prone to chipping or breaking than crowns.
- May require replacement over time.
Financial Assistance for Dental Care
The cost of dental care can be a significant financial burden for many people. Fortunately, there are a number of financial assistance programs available to help cover the cost of fillings and other dental procedures.
Eligibility requirements for these programs vary, but they typically include income and residency restrictions. Application processes also vary, but they typically involve submitting an application form and providing proof of income and residency.
Subsidized Dental Programs
- Medicaid: A government program that provides health insurance to low-income individuals and families.
- CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program): A government program that provides health insurance to children from low-income families.
- Medicare: A government program that provides health insurance to people aged 65 and older, as well as people with certain disabilities.
Dental Discount Plans
Dental discount plans are not insurance plans, but they can help you save money on dental care. These plans typically involve paying a monthly fee in exchange for discounts on dental services.
Dental Schools
Dental schools often offer low-cost dental care to the public. This care is typically provided by students under the supervision of licensed dentists.
Community Health Centers
Community health centers offer a range of health care services, including dental care, to low-income individuals and families.





